

Prostate Cancer: The Most Common Form of Cancer in Males
By: Krunal
Published On: July 26, 2022
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer definition: Prostate cancer is cancer that affects the prostate, which is a small walnut-shaped gland between the penis and the bladder. The prostate gland is responsible for producing the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm and secreting prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a protein that helps semen retain its liquid state and helps with urine control.
Alongside skin cancer, prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. Many types of prostate cancer grow slowly and are confined to the prostate gland, where they may not cause serious harm. These types of prostate cancer may need minimal or even no treatment. On the other hand, there are a few types that are aggressive in nature and can spread quickly.
Early diagnosis of prostate cancer is vital. Therefore, the best chance for successful treatment is when prostate cancer is still confined to the prostate gland.
As per the American Cancer Society (ACS), every 1 in 8 males will be diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point in their life. However, the odds of a patient dying because of prostate cancer are only 1 in 41. This is because of the effective treatment available, especially in the early stages. Routine screening enables doctors to detect cases of prostate cancer before they spread to other parts of the body.
Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
After understanding the meaning of prostate cancer, let’s study its signs and symptoms.
In its early stages, i.e., stage 1, prostate cancer may not show any signs or symptoms. Screening can help detect changes that may indicate cancer. It involves a test that measures PSA levels in the blood. High levels of PSA indicate that cancer may be present.
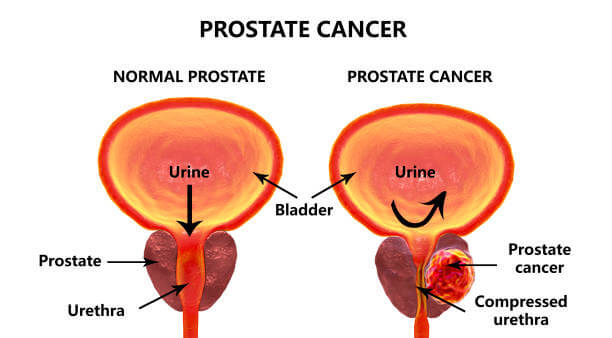
Males who might be suffering from an advanced stage of prostate cancer may experience symptoms such as:
difficulty in urination
a frequent urge to urinate, especially at night
erectile dysfunction
blood in the urine or semen
pain while urinating or during ejaculation
pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
weight loss
What Causes Prostate Cancer?
Even though prostate cancer’s meaning and its signs and symptoms are well known, researchers have been unable to figure out the exact cause of prostate cancer. Doctors know that prostate cancer begins when there is a change in the DNA of the cells in the prostate. A cell’s DNA contains instructions, telling a cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow and multiply more rapidly than normal cells. While other cells would die after a certain shelf life, the abnormal cells continue living.
Also read: Plan Ahead For Bladder Cancer Treatment And Costs
Initially, the changes will be slow and the cells will not be cancerous. However, gradually, the prostate tumor can turn cancerous and can grow to invade nearby tissue. With time, some cancerous cells can break away and spread to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors
While doctors do not exactly know what causes prostate cancer to spread, the following factors may increase the risk of one contracting it:

Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases after the age of 50. It rarely occurs before the age of 45.
Race or ethnicity: Black people are more vulnerable to prostate cancer than white people. In black people, the cancer is also more likely to be aggressive or advanced. Asian and Hispanic people have a lower risk than black or white people.
Family history: If a person’s close relative had a history of prostate cancer, then there is a higher chance of the person developing it himself/herself.
Genetic factors: Inherited features, including changes to the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, may increase the risk of cancer. Men who are born with Lynch syndrome also have a higher risk of contracting prostate and other cancers.
Obesity: Obese people may be at a higher risk of getting prostate cancer compared with people who are fit and healthy. In obese people, the cancer is more likely to be more aggressive and the chances of relapse after initial treatment are also higher.
Other factors that may cause prostate cancer include:
smoking
alcohol consumption
exposure to chemicals, such as the herbicide Agent Orange
sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
vasectomy surgery
How to Avoid Prostate Cancer?
As the old saying goes, “Prevention is better than cure”; the same is true in the case of prostate cancer as well. You can reduce your risk of developing prostate cancer if you:
Choose healthy foods over supplements: Eat a healthy diet comprising fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Fruits and vegetables contain many vitamins and nutrients that can contribute to your health. Also, there is no conclusive evidence that proves supplements play a role in reducing the risk of prostate cancer. Instead, choosing foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals can help maintain healthy levels of vitamins in your body.
Exercise regularly: It’s no secret that exercising regularly can improve your overall health, help you maintain your weight, and revitalize your mood. That’s why you should try to exercise most days of the week. If you’re new to exercise, start slow and work your way up to exercising more every day.
Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is equally important. If your weight is appropriate as per the body mass index (BMI), work to maintain it by choosing a healthy diet and exercising regularly. If you need to lose weight, do more exercise and cut down on your calorie intake each day. If needed, request your doctor to help create a diet plan for weight loss.
Also read: Do These Food Items Cause Cancer?
After understanding the definition of prostate cancer and its risk factors, if you think you are at a very high risk of developing prostate cancer, talk to your doctor right away. He/She may recommend medications or other treatments to reduce the risk. Research suggests that taking 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, including finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart), may help reduce the overall risk of developing prostate cancer. These drugs are helpful in controlling enlargement of the prostate gland and hair loss.
However, there can be adverse effects after taking these medicines. Some evidence indicates that people taking these medicines are at a higher risk of getting a more serious form of prostate cancer (high-grade prostate cancer). If you’re concerned about your risk of getting prostate cancer, consult your doctor.
What Causes Prostate Cancer in Young Males?
The actual reason behind why younger men get prostate cancer is not clear yet. As per researchers, there seems to be a link between your genes and early onset prostate cancer. However, they need to conduct more studies to understand if things like physical activity, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and exposure to things like cancer-causing agents play a role.
If you are diagnosed with prostate cancer when you’re younger, it’s likely to be at a more advanced stage. You’re also more likely to have a lower survival rate than middle-aged men and older men.





 Information
Information Alert
Alert