Imagine a water balloon. It’s a simple yet fitting analogy for a condition known as hydrocele. While it might not involve the joyous splashes of a water balloon fight, it can cause discomfort and concern for those affected. In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of hydrocele, demystifying its meaning, exploring its symptoms, understanding its various types, and shedding light on the cost of treatment in India.
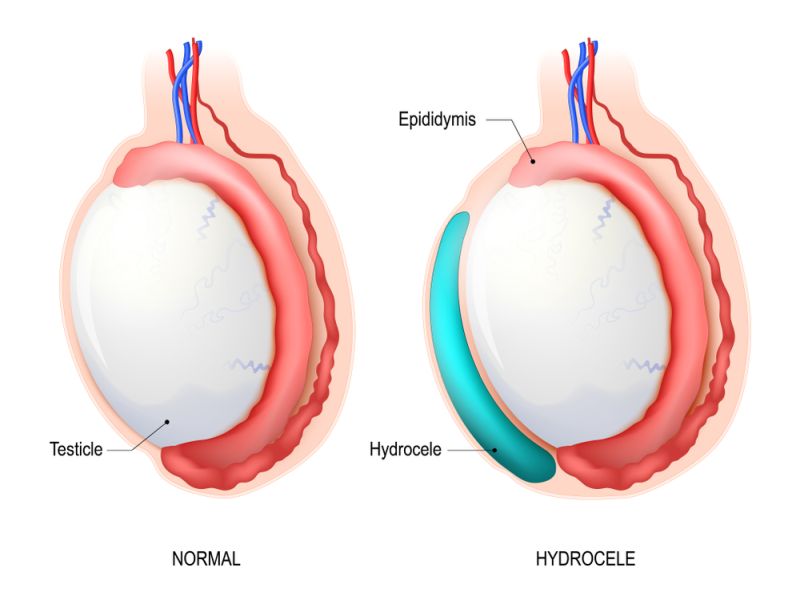
Hydrocele, a term that may sound complex, is a fluid buildup in the sac surrounding a testicle. Simply put, it’s like having a small, painless, water-filled pouch near the testicles. This ailment can affect males of all ages, from newborns to older people, and while it’s not typically dangerous, it can be bothersome and may require medical attention.
One of the primary symptoms of hydrocele is the presence of a painless, swollen scrotum. This swelling is often more pronounced after physical activity or as the day progresses. It’s essential to note that hydrocele typically doesn’t cause any discomfort or pain. However, if you experience sudden, severe scrotal pain, it could be a sign of a different condition and should be promptly evaluated by a medical professional.
Hydroceles come in different forms, mainly based on their causes. The two primary types are congenital and acquired. Congenital hydroceles are typically present at birth and result from the connection between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum not closing as it should. Acquired hydroceles, on the other hand, develop later in life and can be caused by various factors, such as injury, infection, or inflammation.
For many individuals facing hydrocele, one of the most pressing concerns is the cost of treatment. In India, the cost of addressing hydrocele can differ greatly based on various factors, including the type of hospital, the surgeon’s expertise, the region, and the specific treatment method chosen. In general, non-surgical management might be less expensive than surgical options, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
In this blog, we aim to provide a comprehensive and easily understandable guide to hydrocele, addressing its meaning, symptoms, types, and the potential costs of seeking treatment in India. Whether you’re someone facing this condition or simply curious about it, we aim to make this information accessible and insightful. Now, let’s dive deeper into hydrocele, seeking to empower individuals with knowledge and understanding.
Read More: Impactguru hospital finder tool India
Table of Contents
Hydrocele Surgery Cost In India
The estimated cost of hydrocele surgery in India ranges from Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 85,000. However, this is only an approximate figure, and the actual cost may vary depending on your specific case. Therefore, you should consult your doctor and get a personalized quote before undergoing hydrocele surgery.
The cost of hydrocele surgery in India varies depending on several factors, such as:
– The type and severity of the hydrocele: Some hydroceles are simple and easy to treat, while others are complex and require more extensive surgery. For example, if the hydrocele is associated with testicular cancer, the surgery may involve removing the affected testicle and performing a biopsy, which can increase the cost significantly.
– The age and health condition of the patient: Elderly or those with underlying medical state may need more tests and medications before and after the surgery, which can add to the cost. Also, some patients may have complications or infections that require additional treatment or hospitalization.
– The experience and reputation of the surgeon: A skilled and experienced surgeon can perform the surgery more efficiently & safely, reducing the risk of complications and recurrence. A reputed surgeon may also charge more for their expertise and quality of service.
– The type and location of the hospital: The cost of hydrocele surgery can vary depending on whether you choose a private or a government hospital, a multispecialty or a single specialty hospital, or a hospital in a metro city or a smaller town. Generally, private hospitals charge more than government hospitals, multispecialty hospitals charge more than single specialty hospitals, and hospitals in metro cities charge more than hospitals in smaller towns.
– The track record of the hospital: The success rate and patient satisfaction of the hospital can also affect the cost of hydrocele surgery. A hospital that has performed many hydrocele surgeries successfully and has received positive feedback from patients may charge more for its services.
Hydrocele Treatment
A hydrocele usually doesn’t need treatment unless it causes pain, discomfort, or cosmetic concerns. Most hydroceles go away on their own without treatment within six months to a year. However, if a hydrocele persists or becomes large enough to interfere with your daily activities, your healthcare provider may recommend one of the following treatment options:
– Aspiration- It involves inserting a thin needle into the scrotum and draining the fluid from the tunica vaginalis. This procedure can be done in your provider’s office under local anesthesia (numbing medicine). Aspiration can temporarily relieve symptoms, but it does not prevent fluid from accumulating again. There is also a risk of infection, bleeding, or injury to the testicle from aspiration.
– Sclerotherapy– It involves injecting a chemical agent into the tunica vaginalis after aspiration to cause scarring and closure of the sac. This procedure can also be done in your provider’s office under local anesthesia. Sclerotherapy can reduce the recurrence rate of hydrocele, but it may also cause pain, inflammation, or damage to the testicle or spermatic cord.
– Surgery– It involves making a small incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen and removing the fluid-filled sac or closing the opening that allows fluid to flow into the scrotum. This procedure is called a hydrocelectomy and is usually done in a hospital or outpatient surgery center under general anesthesia (you are asleep and feel no pain) or spinal anesthesia (you are awake but numb from the waist down). Surgery is the most effective and permanent way to treat a hydrocele, but it also carries some risks, such as infection, bleeding, hematoma (a collection of blood under the skin), injury to the testicle or spermatic cord, or recurrence of hydrocele.
Hydrocele Diagnosis
Diagnosing a hydrocele typically involves a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and, in some cases, imaging studies. A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac formed around the testicle and may cause scrotal swelling. Here’s how the diagnosis process typically works:
1. Medical History: The doctor will begin by taking your medical history. They will ask questions about your symptoms, when they first appeared, and whether you have any pain or discomfort in the scrotal area. Providing information about your medical history, any previous injuries, or surgeries is also essential.
2. Physical Examination: A physical examination is crucial in diagnosing a hydrocele. The doctor will examine your scrotum, looking for signs of swelling or enlargement. They may also gently shine a light through the scrotum to check if the mass is translucent, a characteristic feature of a hydrocele.
3. Transillumination: Transillumination involves shining a light through the scrotal sac. If the fluid-filled sac is present, it will allow the light to pass through and appear as a fluid-filled, translucent area.
4. Imaging Studies (if needed): Sometimes, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the physical examination is inconclusive. These tests can include:
– Ultrasound: An ultrasound scan can provide detailed pictures of the scrotum and can help confirm the presence of a hydrocele, its size, and other characteristics.
– Blood Tests: It may be recommended to rule out other conditions that could be causing scrotal swelling, such as infections or testicular torsion.
5. Differential Diagnosis: It’s essential to differentiate a hydrocele from other scrotal conditions, such as hernias, testicular tumors, or epididymitis, as the treatment and management of these conditions may differ.
Once the final diagnosis is confirmed, your doctor will evaluate treatment options with you, which may include observation (if the hydrocele is small and not causing discomfort), needle aspiration to drain the fluid, or surgical removal of the hydrocele sac (hydrocelectomy) if it is causing significant pain or has recurred. It’s vital to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a hydrocele or any other scrotal condition, as some of these conditions may require prompt treatment to avoid complications.
Hydrocele Symptoms
A hydrocele is a medical condition that occurs when there is an accumulation of fluid in the scrotum, the sac that surrounds the testes. It is a common condition and is usually not painful. The primary symptom of a hydrocele is swelling of the scrotum. Here are some common symptoms and characteristics associated with hydroceles:
1. Scrotal Swelling: The most noticeable symptom is the swelling of one or both sides of the scrotum. The swelling is typically painless and can vary from small to large.
2. Transillumination: When a light is shone through the swollen scrotum, it may appear to be translucent, which is a characteristic feature of hydroceles.
3. Discomfort or Heaviness: Although hydroceles are usually painless, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or a feeling of heaviness due to the increased size of the scrotum.
4. Enlargement of the Scrotum: The scrotal swelling might be constant, or it could change in size throughout the day, with the scrotum appearing larger in the morning and smaller at night.
5. Difficulty in Palpating the Testes: In some cases, the testes may be difficult to feel or locate within the swollen scrotum due to the fluid buildup.
It’s important to note that while hydroceles are typically harmless, any sudden or severe scrotal pain should not be ignored. Other conditions, such as a hernia, testicular torsion, or infection, can present with similar symptoms, which may require immediate medical attention. If you suspect you have a hydrocele or are experiencing scrotal swelling, it’s important to consult a medical professional for a proper diagnosis & appropriate management.
Hydrocele Meaning & Its Types
A hydrocele is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the scrotum, the pouch of skin that contains the testicles. This condition typically causes swelling and discomfort in the scrotum, which is relatively common, especially in newborns and older men. The term “hydrocele” is derived from two Greek words: “hydro,” which means water, and “cele,” which means swelling or cavity.
There are two main types of hydroceles:
1. Communicating Hydrocele: This type of hydrocele is more commonly seen in infants and young children. It occurs when there is a small, naturally occurring connection between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum that does not close as it should. This connection allows fluid to flow from the abdomen into the scrotum, causing swelling. Communicating hydroceles can sometimes resolve on their own but may require medical intervention, such as surgery if they persist.
2. Non-Communicating Hydrocele (Simple Hydrocele): This type of hydrocele is more commonly seen in adult men. It occurs when fluid accumulates in the scrotum without any direct connection to the abdominal cavity. An imbalance between the production and absorption of fluid in the scrotal sac typically causes non-communicating hydroceles. These hydroceles can be painless and may fluctuate in size, but they usually don’t go away on their own. Surgical treatment may be necessary to drain the fluid and repair any underlying issues.
Hydroceles can be distinguished from other scrotal conditions, such as hernias, by their characteristic swelling that can be transilluminated, meaning that a light shined through the scrotum will pass through the fluid-filled sac, making it appear as a fluid-filled sac or mass. It’s best to connect with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis & to determine the most appropriate treatment for a hydrocele, which may involve observation, aspiration of the fluid, or surgery, depending on the type and severity of the hydrocele.
Causes Of Hydrocele
A hydrocele is an ailment characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the scrotum, the pouch of skin that holds the testicles. It can develop in males of all age types, including newborns, and is usually painless. The leading causes of hydroceles include:
1. Congenital Hydrocele: This is the most common cause of hydroceles in newborns. During fetal growth, the testicles descend from the abdomen into the scrotum, and a small sac accompanies them, which is supposed to close off and reabsorb the fluid. If this process doesn’t happen as it should, a hydrocele may develop. It often resolves on its own in the first year of life.
2. Secondary Hydrocele: In older boys and adult men, hydroceles can develop due to various conditions or injuries. These may include:
– Infection: Infections in the scrotum or surrounding areas can lead to the buildup of fluid.
– Trauma: Injury to the scrotum can cause a hydrocele.
– Inflammation: Inflammation of the epididymis or testis can lead to fluid accumulation.
– Tumors: Tumors in the scrotum can block fluid flow and cause a hydrocele.
– Hernia Surgery Complications: In some cases, hydroceles can occur as a complication of hernia surgery.
3. Idiopathic Hydrocele: In some cases, the exact cause of a hydrocele may not be determined. These are known as idiopathic hydroceles.
While hydroceles are usually not painful, they can cause discomfort or be unsightly. If a hydrocele is causing significant distress or if it doesn’t resolve on its own, medical intervention may be necessary. It’s better to consult a medical professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management if you suspect a hydrocele.
What To Expect Before, During & After Hydrocele Surgery?
Hydrocele surgery is a medical procedure to treat a hydrocele, a buildup of fluid around the testicle. Before, during, and after the surgery, there are certain things you can expect:
Before the Surgery:
1. Consultation: You will have a discussion with a urologist or surgeon to discuss the surgery, your medical history, and any concerns you may have. They will explain the medical procedure & answer any questions you might have.
2. Preoperative Preparation: Your doctor will provide specific preoperative instructions, including fasting for a certain period before the surgery and discontinuing certain medications. You may also be asked to shower and cleanse the surgical area with a special soap.
3. Anesthesia: Most hydrocele surgeries are performed under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia. Your healthcare team will discuss which option is best for your case.
During the Surgery:
1. Procedure: There are different techniques for hydrocele surgery, but the most common method is a surgical cut (incision) made in the scrotum. The fluid is drained, and the sac around the testicle is either removed or stitched closed to prevent fluid from accumulating again.
2. Duration: The surgery usually takes around 30 minutes to an hour, but the actual time may vary depending on the case’s complexity.
After the Surgery:
1. Recovery Room: After the surgery, you will spend some time in the recovery room under close medical supervision.
2. Discomfort: You may experience discomfort, pain, or swelling in the scrotal area after the surgery. Your doctor will recommend pain medications to manage this.
3. Hospital Stay: Hydrocele surgery is often done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day. In some cases, an overnight stay may be required.
4. Rest and Activity: It’s important to rest & avoid vigorous activities for a few days to allow the surgical site to heal properly. You should also avoid heavy lifting for several weeks.
5. Follow-up Appointments: You will have follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor your progress and ensure proper healing. Sutures, if used, may be removed during one of these visits.
6. Swelling and Bruising: Some degree of swelling and bruising is expected after the surgery, but it should gradually improve over time.
7. Complications: While complications are rare, they can include infection, bleeding, scrotal hematoma (a collection of blood in the scrotum), and recurrence of the hydrocele.
8. Resumption of Normal Activities: Your doctor will advise you when it’s safe to resume normal activities, including sexual activity and exercise.
It’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully during the entire process to ensure a successful recovery. If you experience severe pain, signs of infection, excessive swelling, or any other concerning symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Keep in mind that individual experiences may vary, and your doctor will provide you with personalized guidance for your specific case.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydrocele is a common condition that affects a significant number of individuals, both young and old, in India and around the world. This blog has delved into the meaning, symptoms, types, and cost of treating hydrocele in India, offering a comprehensive understanding of this condition and the factors associated with its management.
Hydrocele, in simple terms, refers to fluid accumulation in the sac surrounding the testicles. This can lead to discomfort, swelling, and, in some cases, pain. Although hydroceles are generally harmless, they can cause discomfort and impact one’s quality of life.
We explored the different types of hydroceles, with the most common being the simple hydrocele. While simple hydroceles do not usually require surgical intervention, other types, like communicating hydroceles, may necessitate more complex treatment approaches. Understanding the kind of hydrocele one has is crucial for determining the appropriate course of action.
When it comes to the cost of managing hydroceles in India, it is clear that the financial aspect is a significant concern for many. The cost varies based on factors like the type of hydrocele, the chosen treatment method, and the healthcare facility. It’s important to note that the cost of surgery and related expenses can add up, making it essential to research and plan accordingly. Government healthcare schemes and insurance coverage can play a vital role in alleviating some of the financial burdens associated with hydrocele treatment.
In summary, hydrocele is a condition that affects many individuals and can impact their quality of life. By recognizing the meaning and symptoms of hydrocele, as well as the different types, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options. Additionally, understanding the costs of managing hydrocele in India is crucial for financial planning. Ultimately, seeking medical advice, exploring treatment options, and taking steps to address this condition are essential for those affected by hydrocele.
Hydrocele surgery can be expensive, and many individuals may not have the necessary funds to cover the costs. A fundraising platform provides a medium for them to access financial support. It brings together a community of supporters, friends, and family who can contribute towards the cause. People are often willing to help when they know the funds are going directly towards a medical necessity.












