Have you ever wondered what truly remains after we’re gone? Most of us leave behind memories — but through body parts donation, we can also leave behind life itself.
Body part donation in India is among the most selfless acts a person can choose. Whether it’s donating organs after death or pledging your whole body for medical research, each contribution can save lives, restore vision, improve mobility, and train future doctors.
India faces a major organ shortage crisis, where thousands wait for transplants every year. Every registered organ or body donor becomes a lifeline for someone in need. Fortunately, awareness is rising, and more people are now signing up for donor cards and registering for full-body donation after death.
This 2025 guide explains everything about body parts donation in India — how it works, the difference between organ donation and body donation, the registration process, and how you can help others even beyond life.
Read More: Liver Size: Normal Range and Health Indicator
Click here to Find Best Hospitals near you.

Table of Contents
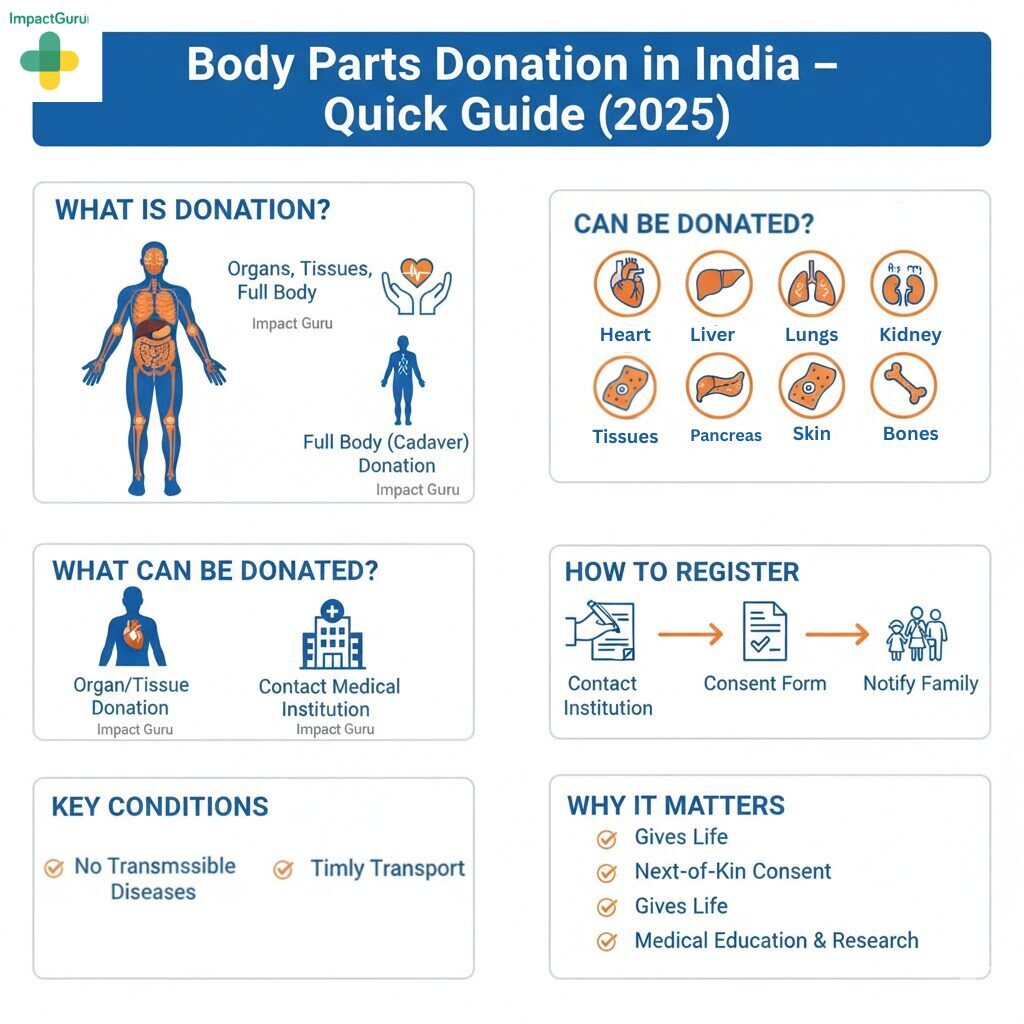
What Is Body Donation and Cadaver Donation?
Body donation, also known as whole body donation, is the act of voluntarily donating your entire body after death for medical education and research. It plays a vital role in helping medical students study human anatomy and enabling researchers to develop new surgical techniques, treatments, and life-saving innovations.
In contrast, organ donation or body parts donation focuses on donating specific organs — such as the heart, liver, or kidneys to save or enhance the lives of patients in need of transplants.
Cadaver donation refers to donating the entire human body (also called a cadaver) for educational and scientific purposes. Individuals who choose this path are known as cadaver donors. Their contribution helps train surgeons, advance medical research, and improve future healthcare outcomes.
In India, where medical institutions often face a shortage of cadavers for study, full-body donation programs are essential for advancing healthcare education. Meanwhile, crowdfunding platforms like ImpactGuru help families raise funds online for organ transplants, connecting the spirit of giving in both life and afterlife.
Click here to Calculate the Cost of your Treatment.
Body Parts Donation vs. Full Body Donation
While both organ donation and full body donation play a vital role in serving humanity, they contribute in distinct yet equally meaningful ways.
Organ donation after death involves donating specific organs such as the heart, liver, kidneys, lungs, pancreas, and corneas to patients in need of life-saving transplants.
A single organ donor can save up to eight lives and improve the quality of life for dozens more through tissue donation.
In contrast, full body donation—also known as cadaver donation—means donating your entire body to medical education and research. These donations allow future doctors to study real human anatomy, perform surgical training, and make medical advancements that benefit thousands of patients over time.
It’s important to understand that both donations usually cannot be done together. Once organs are removed for transplant, the body may no longer be suitable for medical study.
That’s why individuals often choose to pledge either organ donation or full body donation, based on their personal wishes and how they wish to contribute to society.
Read More: Liver Transplant Donor Criteria: Complete Guide for India
Which Human Organs Can be Donated?

Many people are surprised to learn just how many human organs can be donated after death — and how many lives a single organ donor can save.
The major organs that can be donated include:
- Heart Donation – Helps patients suffering from end-stage heart failure.
- Liver Donation – The liver is the only organ that can regenerate; a part or the whole liver can be transplanted to save lives.
- Kidney Donation – Since humans have two kidneys, one or both can be donated, giving two people freedom from dialysis.
- Lung Donation – Vital for patients struggling with chronic or end-stage lung diseases.
- Pancreas Donation – Beneficial in treating severe or advanced cases of diabetes.
In addition to organs, several tissues can also be donated, such as corneas, skin, bones, tendons, and heart valves — all of which can dramatically improve the quality of life for recipients.
Understanding which organs and tissues can be donated is essential for anyone considering body parts donation.
Even if a person isn’t eligible for full body donation, their organs and tissues can still offer others a second chance at life through organ donation after death.
Every donated organ is more than a medical gift — it’s a renewed hope, often the only chance of survival for someone waiting on the transplant list.
How to Become an Organ Donor?
While organ donation helps save lives through transplants, body donation contributes to medical education and research, allowing future doctors to study real human anatomy and practice surgical procedures.
If you wish to donate your body after death, here’s how the body donation process works in India:
1. Understand the Purpose of Body Donation
Donated bodies are used for medical study, surgical training, and anatomical research in government-approved medical colleges.
Unlike organ donation, which benefits patients directly, whole-body donation supports long-term healthcare by helping doctors and researchers develop better medical knowledge and surgical techniques.
2. Contact a Recognized Medical Institution
Body donation in India is usually coordinated through a nearby medical college or teaching hospital.
Steps:
- Identify a government-recognized medical college or anatomy department near your area.
- Contact their body donation unit and request details or forms for whole-body donation.
- Note that procedures may vary slightly between institutions.
3. Fill Out the Body Donation Consent Form
Download or collect the Body Donation Consent Form from the medical college’s website or office.
Complete and submit it as instructed (some may require notarization).
Once registered, you’ll receive an acknowledgment letter or donor certificate confirming your pledge.
4. Inform Your Family and Keep Documents Accessible
After death, your next of kin or family member must contact the medical college to fulfill your wish.
Discuss your decision with your family in advance and keep copies of your registration form and donor certificate in an easy-to-find place.
5. Understand the Conditions That May Affect Donation
Sometimes, bodies cannot be accepted for medical study due to:
- Infectious diseases such as HIV or hepatitis
- Severe physical damage from major accidents
- Transportation issues or limited storage capacity
Always confirm eligibility and procedures with the institution, just as there are medical criteria for organ and tissue donation (e.g., liver transplant donor requirements).
6. No Financial Cost Involved
Body donation in India is entirely voluntary and free of cost.
In most cases, the medical college arranges transportation of the body and conducts scientific last rites respectfully and ethically.
How to Register for Organ or Body Donation in India
Becoming a donor begins with one clear step — officially expressing your consent. Here’s how you can register for organ donation or full body (cadaver) donation in India:
Organ Donation Registration in India
Here’s how you can register as an organ donor:
- Visit official government websites such as the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO).
- Fill out the online organ donation pledge form with your details and declaration of consent.
- After submission, you’ll receive an Organ Donor Card, which states your wish to donate organs after death.
- While the card is not legally binding, it helps both medical teams and your family know your intent.
- Inform your family members about your decision — their cooperation will be essential during the donation process.
- Meet the eligibility criteria for organ donation. For example, a healthy liver with normal size and weight can be donated to another person, but a medical evaluation determines final suitability.
Body (Cadaver) Donation Registration in India
If you wish to donate your entire body to medical science, follow these steps:
- Contact the government or medical college hospitals such as AIIMS, PGIMER, KEM Hospital, or your nearest state medical college.
- Fill out the body donation registration form (each institution may have a slightly different format).
- Submit your personal details and next-of-kin information as required.
- Keep a signed copy of your form and inform your family about your decision to ensure cooperation when the time comes.
Important Notes
- Family Consent: Even after registration, most institutions require next-of-kin consent at the time of death.
- Age Limit: There’s no fixed age limit for organ donors. For body donation, most colleges accept donors aged 18 years and above.
- Costs: Donation is entirely voluntary and free. Transport and documentation are usually handled by the hospital or medical college.
- Carry Your Organ Donor Card: Though not legally binding, it helps inform medical authorities and your family of your decision.
- Change of Mind: You can withdraw your consent anytime by notifying the institution where you registered — your decision will always be respected.
By registering, you’re making a powerful commitment — to give life after life.
Organizations like Impact Guru also support transplant patients through crowdfunding for organ transplant procedures, allowing families to raise funds for life-saving treatments and spread awareness about donation.
Conclusion
Organ and body donation is a selfless act that gives someone else a second chance at life or helps advance critical medical education and research. Whether you choose to perform body parts donation or pledge your body to science, your contribution leaves a lasting impact.
Moreover, for families facing expensive transplant surgeries, crowdfunding websites like ImpactGuru can be a lifeline. While your donation saves lives, someone else might be waiting for financial help to receive it. By pledging, sharing, or donating, you become part of this powerful circle of care.
FAQs on Body Parts Donation
Generally, no. If organs are harvested for transplant, the body may not qualify for cadaver donation due to surgical intervention and time sensitivity. Most individuals choose to donate either their organs or their entire body, not both.
For organ donation, there is no strict age limit. Each case is evaluated individually based on organ condition and suitability. For body donation, most institutions accept donors aged 18 and above. Some may have an upper limit, often around 75–80 years.
Body parts donation involves voluntarily giving organs or tissues—such as the heart, kidneys, liver, lungs, pancreas, corneas, skin, and bones—to save lives or aid medical research.
Organ donation refers to transplanting specific organs to recipients, while body donation (cadaver donation) involves donating the entire body for medical education and research.
Anyone aged 18–65, in good health, and without transmissible diseases can pledge to donate organs or their entire body.
You can register by filling out a consent form at a government-recognized medical college or hospital, or by visiting the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO) website.
Donated organs are transplanted into patients in need, while the entire body is used for medical education and research, helping train future doctors and advancing medical science.












