Varicose veins affect millions of people throughout the world and are a regularly misunderstood medical issue. The prominence of these veins creates an appearance that seems superficial, yet their existence causes genuine pain along with major medical issues. The guide provides in-depth information about everything regarding varicose veins, starting with their basic characteristics and explanations of both origins and methods for detection, as well as healing procedures and protective steps.
Table of Contents
- Varicose Veins Meaning
- Varicose Veins Description
- Varicose Veins Symptoms
- Varicose Veins Stages
- Types Of Varicose Veins
- What Causes Varicose Veins?
- Can Varicose Veins Lead To Serious Health Implications?
- Are Varicose Veins Common, & Who Gets Affected The Most?
- Diagnosis and Tests for Varicose Veins
- Varicose Veins Treatment
- How To Prevent Varicose Veins?
- Conclusion
- FAQs Related To Varicose Veins
Varicose Veins Meaning
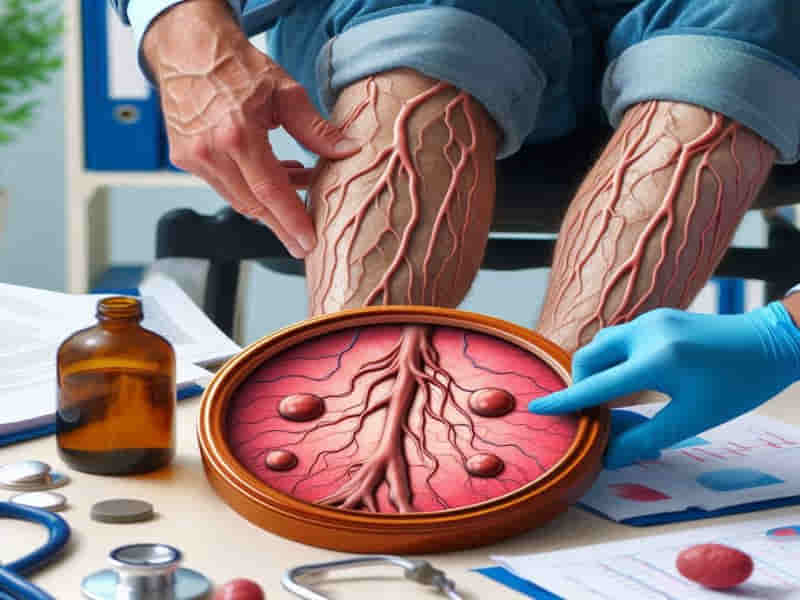
Varicose veins develop into dilated and distorted veins that can be seen below the skin. These dilated veins generally appear in the lower areas of the body, especially the legs and feet. “Varicose” is a term inferred from the Latin word ‘varica’, which implies bulging. It is utilized to depict the appearance of these veins, which are characteristically bent and bulging in nature. People usually seek medical assistance purely due to the unappealing physical manifestation of varicosities.
Varicose Veins Description
Healthy veins contain functioning valves that direct blood forward toward the heart. Because of valvular insufficiency, either through damage or weakness, the veins accumulate blood, leading to the visible enlargement of the veins in varicose veins. The medical condition known as venous reflux causes blood to flow backward, which results in varicosities becoming bulged and twisted. Excessive pooling of blood continues to expand vein walls until the condition becomes worse.
Varicose Veins Symptoms
Some individuals with Varicose veins experience no symptoms, while others might go through the same medical condition with symptoms that are mild to severe. These symptoms include:
1. Throbbing Pain: The discomfort increases when you sit or stand for long periods because bloodstream concentration rises inside varicose veins. People who experience varicose vein pain describe it as either an uncomfortable dullness or waves of painful pressure.
2. Heaviness In The Legs: A feeling of heaviness or fatigue, especially after physical activity. Walking, together with other daily activities, becomes challenging when heaviness occurs.
3. Swelling in Legs & Ankles: The affected veins’ impaired circulation leads to a condition called edema that produces swelling in both feet and ankles. People with this condition tend to observe swelling the most when they lie down after a day of standing or sitting.
4. Burning Or Itching Sensation: The affected veins produce a burning sensation in combination with itching symptoms. Verbal itching requires severe attention since intense scratching creates more discomfort in the affected skin area.
5. Discoloration of Skin & Ulcers: The most severe varicose vein manifestations include darkening together with skin thickening and dryness, which results in skin ulcers. Venous ulcers develop as an effect of poor circulation because of weakened blood flow in the body, and they show difficulty in healing.
Varicose Veins Stages
There are six stages of Varicose Veins, and it is crucial to know the stages at which the above-mentioned symptoms start to appear for more effective management and treatment.
- During Stage 1, the patient may exhibit small veins on their skin, known as telangiectasia or reticular veins. Generally, there are no significant physical symptoms, and the primary concern at this stage is cosmetic.
- In Stage 2, the subcutaneous layer reveals visible, twisted, and enlarged varicose veins. Patients may experience calf heaviness, along with cramps and muscle pulling that occurs during prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- Stage 3 is characterized by leg swelling and calf discomfort, coupled with pain associated with venous insufficiency.
- In Stage 4, the skin undergoes changes, such as darkening, drying out, and becoming thinner. There is often chronic inflammation of the skin, particularly above the ankles.
- Individuals in Stage 5 may exhibit skin scarring on their legs near the ankles, resulting from previously healed trauma.
- Stage 6 is marked by the presence of leg wounds, especially near the ankles. These wounds typically have uneven edges and feature a deep center that remains damp and red, with chronic inflammation affecting the surrounding area.
Types Of Varicose Veins
Different types of varicose veins have distinct features that can be categorized into three main types.
1. Trunk Varicose Veins: The great saphenous vein and the small saphenous vein, along with the other major superficial veins of the leg, exhibit trunk varicose veins, which appear as large, rope-like structures. The most noticeable type of varicosities causes painful sensations, accompanied by throbbing and a heavy feeling of discomfort. The larger dimensions of these veins increase the likelihood of developing phlebitis.
2. Reticular Veins: Under the skin, smaller blue-purple veins, known as reticular veins, are visible. These veins are informally called “spider veins,” although medical professionals refer to this condition as telangiectasia. Reticular veins are primarily seen as cosmetic defects, but they can occasionally cause minor discomfort, such as aching and burning sensations.
3. Telangiectasia: Spider veins develop into telangiectasia, which presents as thin red or purple, web-like veins on the surface of the skin. These visible blood vessels primarily appear on the face and legs without causing any significant health issues. They are most commonly observed when people spend time in the sun or undergo hormonal changes.
What Causes Varicose Veins?
1. Weakened Or Damaged Valves: The main valve dysfunction stands as the primary cause that leads to endothelial fluid accumulation inside veins. Resistance failure of the valves occurs because of genetic factors, age-related reasons, or unrelated causes.
2. Family History: People with an inherited genetic tendency toward varicose veins risk an increased probability of developing this condition. People who inherit varicose veins from their parents or grandparents have higher chances of developing these veins themselves.
3. Age: The normal weakening of valves and decreased elasticity in veins that occurs during the aging process represents a significant risk factor for the development of varicosities. All human bodies show typical aging characteristics.
4. Pregnancy: The hormone progesterone elevations during pregnancy lead to vein wall loosening. The expanding uterus forces the pelvis and lower legs as it grows, which results in varicosities.
5. Excess Weight: The pressure from obesity increases the difficulty for the legs to return blood to the heart through their veins.
6. Standing Or Sitting For A Long Time: The combination of prolonged standing or sitting prevents normal blood flow due to non-functioning calf muscles that would usually assist in pumping blood back to the heart.
Can Varicose Veins Lead To Serious Health Implications?
Patients typically overlook this medical issue as a cosmetic condition, but these swollen or enlarged veins can trigger vital health conditions.
1. Phlebitis: Inflammation of veins known as phlebitis produces three main symptoms, which include pain together with redness, swelling, and heat sensations. Signs of superficial thrombophlebitis normally remain nonthreatening, although there is a risk of developing DVT in some patients.
2. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): DVT forms when blood clots develop in deeper leg veins, thus posing a severe threat to life. The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) include uncomfortable, intense pain and painful swelling alongside the related tenderness in the leg. Blood clots contain the risk of creating dangerous medical problems when pieces of clots dislodge and travel to the lungs to form pulmonary embolisms.
3. Venous Ulcers: The skin develops open sores referred to as venous ulcers because of inadequate blood circulation. The skin ulcers that develop from poor circulation prove hard to treat while causing persistent pain, and they are prone to infection.
4. Bleeding: Any ruptured varicose veins that appear near skin surfaces often result in bleeding, which may become heavy. The bleeding condition does not typically pose fatal risks to patients.
Are Varicose Veins Common, & Who Gets Affected The Most?
The prevalence rates of varicose veins exist in 20-30 percent of adults and include both men and women as potential patients. A large portion of adults experience varicosities since they affect one-fourth of the adult population. Varicose veins affect both sexes but occur frequently in female patients due to hormonal changes and pregnancy. Age serves as an essential risk factor because people tend to develop varicose veins as they grow older.
Diagnosis and Tests for Varicose Veins
Varicose vein diagnosis consists of two components, which are physical examination and analysis of medical history for each patient. The severity of such conditions requires particular tests for complete assessment.
1. Duplex Ultrasound: A Duplex Ultrasound test creates vein pictures through sound waves while monitoring blood flow in a non-surgical manner. The diagnostic tool shows indications of weakened valves together with blood clots and other irregularities in vein structures. This method is often regarded as a top-tier diagnostic method.
2. Venography: The procedure of venography requires that a physician injects contrast dye into the veins before taking X-ray images to see the veins’ structure and blood pathway. Other imaging tests need to be inconclusive for medical professionals to perform this procedure. If other imaging tests prove to be inconclusive, medical professionals opt for this method.
Varicose Veins Treatment
The therapy options for varicose veins differ according to what stage the condition is at and how much the patient experiences symptoms. Some common varicose vein treatments include:
1. Compression Stockings: Specialized compression stockings create leg pressure that accelerates blood flow and decreases leg area swelling. They serve as an initial therapy choice for people who have varicose veins.
Side Effects: Wearing compression stockings may result in several common side effects, including skin irritations that produce itchiness or cold-hot sensations along with redness and pain or discomfort of the skin.
2. Sclerotherapy: Medical professionals inject a solution into the varicose veins using sclerotherapy to trigger scarring that leads to vein fading. The medical procedure treats small to medium-sized varicose veins along with spider veins through a minimally invasive approach.
Side Effects: Bruising and stinging and the development of discoloration serve as typical side effects that occur due to injections during sclerotherapy procedures. The minor adverse effects that develop from treatment become better within a short period.
3. Laser Treatment: Laser energy serves to heat and eliminate damaged veins through treatment. Medical providers can carry out these procedures by injecting solutions through the skin for spider veins and small varicose veins, as well as through the vein for treating larger varicosities.
Side Effects: Side effects of laser treatment for varicose veins consist of skin redness alongside temporary burning or stinging sensations, minor bruising, swelling, itching, discoloration changes, and extremely rare blistering occurrences.
4. Use of Radiofrequency: The varicose veins receive thermal energy from radiofrequency mechanisms to close them during this procedure. Doctors perform this procedure by using methods that resemble those in laser treatment.
Side Effects: The most typical side effects of radiofrequency treatment include bruising with swelling along with discomfort at the treatment location as well as numbness, tingling sensations, and redness.
5. Surgery: Both the removal and repair of varicose veins require surgery when the condition becomes severe. The treatment options include vein stripping to eliminate the saphenous vein along with ambulatory phlebectomy, which removes small varicosities by making small cuts on the skin.
Side Effects: Drvolar surgery holds possible risk, which include pain and bleeding alongside infection and scarring of the treatment area. Little potential exists for developing DVT as one of the treatment risks.
Getting medical advice about the varicose veins treatment procedure and possible treatment side effects should be your first step before starting any medical procedure.
How To Prevent Varicose Veins?
- Weight management to keep a healthy body weight brings about a significant reduction of vein pressure.
- Physical movement stimulates blood flow and strengthens your leg muscles to efficiently return blood toward your heart.
- Make regular pauses to walk and raise your legs above heart level when you stay in extended standing or sitting positions. You should stand with alternate legs to reduce the pressure on your veins during long standing periods.
- Resting your legs elevated above the heart level promotes better blood return to the heart.
- Compression stockings serve as a tool to enhance venous support and circulation, especially when carrying out prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- The importance of not wearing tight clothing is because such clothes place restrictions on blood flow, primarily around the waist and leg areas.
Conclusion
Varicose veins frequently appear as a common medical condition that produces discomfort in some patients and occasionally triggers worse medical problems. Identifying both the root causes and observable symptoms together with treatment solutions for varicosities will help establish proper management approaches. People need to talk to healthcare professionals for a professional diagnosis before receiving individualized treatment recommendations, even though lifestyle changes help stop varicose vein progression. Medical intervention at an early stage produces two advantages: decreased discomfort and reduced risk of complications, which enhance total life quality. Do not postpone checking with medical experts if you notice signs and symptoms of varicosities. For adequate treatment management, you must receive a correct medical diagnosis because self-treatment proves dangerous for effective care. Through evaluation, your doctor will determine how serious your condition is while coming up with the proper treatment that suits your needs.
If you ever find yourself in need of urgent funds for critical healthcare, visit the Best Crowdfunding Platform in India – Impact Guru to see how crowdfunding can make a difference.
FAQs Related To Varicose Veins
- Are Varicose Veins Dangerous?
Most instances of varicose veins pose no threat to health, although they do require medical intervention when these conditions surface: blood clots, ulcers, or bleeding.
- How To Prevent Varicose Veins?
The prevention of varicose veins starts with regular exercise along with weight control, leg elevation, and reduction in sitting and standing durations combined with compression stockings usage.
- How To Avoid Varicose Veins In Legs?
An active lifestyle, along with avoiding lengthy periods of leg crossing, should be combined with supportive footwear while incorporating leg elevation exercises for vein pressure relief.
- When To Worry About Varicose Veins?
See a doctor immediately for severe pain, swelling, skin discoloration or open sores, and sudden leg swelling since these symptoms suggest deep vein thrombosis.
- Which Doctor Should To Consult For Varicose Veins?
You can consult vascular specialists, phlebologists, as well as dermatologists for Varicose vein treatment.
- What Food To Avoid For Varicose Veins?
You should minimize the consumption of salted processed foods along with sugary snacks, alcohol, and unhealthy fats since these items can damage vein health and reduce blood circulation.
- Are Varicose Veins Genetic?
Your risk of varicose veins increases when you come from a family background of this condition because genetics significantly influence the development of varicosities.
- Are Varicose Veins Hereditary?
The presence of varicose veins in families happens because people inherit weak vein walls together with damaged valves.
- Can Varicose Veins Cause Death?
Untreated varicose veins present an extremely rare risk for two severe complications that might become fatal: deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.












