Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) plays an important role in controlling thyroid function. It regulates the production of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), which affect metabolism, energy levels, and overall growth and development. To ensure your thyroid health, a TSH test is taken, especially if you face problems like fatigue, sudden weight changes, and extreme mood swings. But what does the TSH level mean? What is the TSH normal range, and how do different TSH levels affect our health? Understanding the TSH normal range is vital for diagnosing thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. However, for patients who cannot afford regular tests and treatment, crowdfunding in India can help cover ongoing medical expenses.
In this blog, we will cover the TSH meaning, TSH normal value, guide you with the test, and share some tips to maintain balanced TSH levels. If you are getting your TSH test and need guidance or just want to understand your Thyroid health better, this blog can be helpful. A TSH test is simple and affordable, but long-term thyroid care may require frequent monitoring and medication. Patients can raise money online to manage these recurring costs without financial stress.
Table of Contents
What is Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)?
Stimulating Hormone is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland in the brain. Its purpose is to stimulate the thyroid gland to release the thyroid hormones that control the metabolism, body temperature, and overall energy levels.
What Does TSH do?
It signals the thyroid gland to release 2 hormones:
– T3 (triiodothyronine), which influences metabolism, heart rate and digestion.
– T4 (thyroxine) that helps to regulate energy production and body functions.
How Does TSH Work?
When T3 & T4 hormones are low, the pituitary gland releases more TSH to stimulate the thyroid and boost its performance. Likewise, when T3 & T4 levels are high, then it reduces the TSH production to slow things down and to maintain a balance. The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone in response to the level of thyroid hormones to maintain this balance. Trusted crowdfunding platforms provide families a safe and transparent way to gather funds for diagnostic tests, consultations, and thyroid treatments, ensuring timely medical care.
Low levels of TSH indicate hypothyroidism, and high levels of TSH indicate hyperthyroidism.
Now that we know the meaning of TSH and how it works, let us understand the normal TSH values for different individuals as per age and other factors.
TSH Normal Range
As per the American Thyroid Association, the TSH normal value ranges from 0.4 to 4.0 mlU/L. Even though many labs use these reference values, another study done by JCEM showcases separate Normal TSH values for adults by age:
TSH Normal Range for Adults
18-50 years = 0.5 to 4.1 mlU/L.
51-70 years = 0.5 to 4.5 mlU/L.
71-90 years = 0.4- 5.2 mlU/L.
TSH Normal Range for Pregnant Women
As per a study conducted by IJEM, one in eight college-going females is facing thyroid problems. Women are at higher risk of TSH disbalance due to menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. With thyroid disorders becoming increasingly common, crowdfunding India has emerged as a reliable support system for patients who need continuous financial help for lab tests and medicines.
As per perinatology, the TSH normal values for pregnant women are as follows:
First Trimester – 0.6 – 3.4 mlU/L
Second Trimester – 0.37 – 3.6 mlU/L
Third Trimester – 0.38 – 4.04 mlU/L
TSH Normal Range for Children
Infants – 1.6 to 24.3 mlU/L
2 weeks to 20 weeks – 0.58 to 5.57 mlU/L
20 weeks to 18 years – 0.55 to 5.31 mlU/L
Factors Affecting Normal TSH Value
The TSH levels are high in infants and gradually reduce as the child grows.
Various factors can affect the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone in addition to age, gender, and pregnancy status. These might include environmental, genetic, and intrinsic factors. Here is the list of the potential factors:
- Iodine intake – Iodine is necessary for TSH production. Deficiency or excessive intake can lead to abnormal TSH levels.
- Medications – Some medications, like steroids or antidepressants, can influence TSH values.
- Illness – Any pituitary disorder and chronic illnesses will also affect normal TSH values.
- Smoking – Smoking can lead to lower TSH levels.
- Time of the day – TSH levels follow a certain daily routine. They reach their height at night around midnight and come to their lowest point during the afternoon.
- Stress and Lifestyle – Factors like lack of sleep, poor diet, fasting, and lack of exercise can also imbalance normal TSH values.
What do High and Low TSH Levels Mean?
Meaning of High Levels of TSH
High TSH indicates Hypothyroidism and is caused by low production of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) hormones.
Causes of High TSH
The most common cause of Hypothyroidism is the underdiagnosis of thyroid disease or people not getting treatment for the same. In this situation, the thyroid gland produces an insufficient amount of hormones, leading to high levels of TSH production. Choosing a secure crowdfunding platform in India allows patients to share their story, reach more donors, and get quick financial aid for TSH tests and related treatments.
More causes can include:
- Hashimoto’s disease
- Thyroiditis
- Iodine deficiency
- Radiation therapy
- Thyroidectomy
Symptoms of High TSH
- Fatigue
- Swelling on the face and neck area
- Weight gain
- Hair thinning
- Slow heart rate
- Joint and muscle pain
- Dry skin
- Fertility problems faced by women
- Constipation
- Irregular periods
Treatment
Treatment for hypothyroidism includes taking hormone replacement therapy, named levothyroxine. It replaces the thyroxine hormone that your thyroid gland is not producing enough. You will have to take this medicine lifelong. You should get a TSH test every year in order to know your hormone condition and correct medical dosage.
Low Levels of TSH Meaning
Low TSH indicates Hyperthyroidism and is caused due to high production of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) hormones.
Causes of Low TSH
- Excess iodine intake
- Excess thyroid medication
- Pregnancy related changes
- Grave’s disease
Symptoms of Low TSH
- Weight loss
- Irritability and mood change
- Irregular or rapid heartbeats
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Shaky hands and muscle weakness
Treatment
There are several treatment options available for hyperthyroidism, the right option depends on your age, health, and the severity of your condition. Here is the breakdown for each of them:
Anti-thyroid medicine – Drugs like methimazole and propylthiouracil help lower hormone production. This treatment usually lasts 12–18 months. Some people go into long-term remission, but symptoms can return.
Radioiodine Therapy – This oral treatment shrinks the thyroid over time. However, it may lead to hypothyroidism, which means you’ll likely need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement afterwards.
Thyroidectomy (Surgery) – This is usually the least common treatment option for hyperthyroidism. This surgery removes part or all of the thyroid. It’s less common but may be an option for pregnant individuals or those who can’t take medicines or radioiodine.
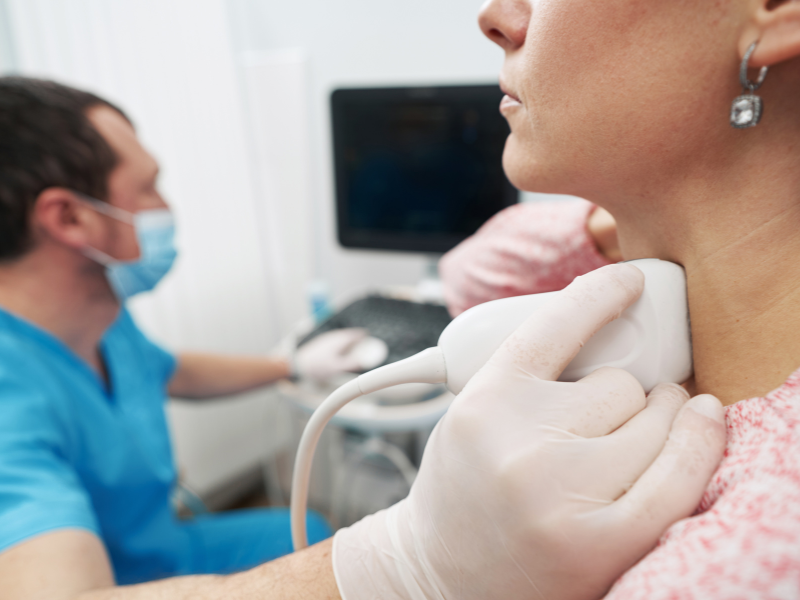
What is the TSH Test and How Does It Work?
To determine the level of thyroid stimulating hormone in your blood, the TSH test is performed. This test helps in evaluating your body’s thyroid functions and the diagnosis of medical conditions, including underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). In this test, your blood sample will be taken and sent to the laboratory for testing and evaluation.
Who Should Take the TSH Test?
If you find yourself experiencing any of the symptoms we mentioned earlier, you should definitely get a TSH test to ensure your thyroid health.
For this test, you don’t need any preparation. But make sure you inform your doctor about any over-the-counter medications you are taking to ensure your test analysis is accurate. Additionally, if you take thyroid medication, don’t take the daily dose prior to the test.
TSH Test Interpretation
As per the American Association of Thyroidology, these values can help you interpret your TSH test results:
Subclinical hypothyroidism – 4.7 to 10 mlU/L
Primary hypothyroidism – More than 10 mlU/L
Subclinical hyperthyroidism – 0.1 TO 0.5 mlU/L
Primary hyperthyroidism – Less than 0.1 mlU/L
However, it is important to understand that even though the TSH test has its own importance, it is more useful when used with reference to the T3 and T4 test results.
This table will help you understand it better:
| TSH | T3/T4 | What it Implies |
| High | Low | This implies primary hypothyroidism. It often occurs due to Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis |
| Low | High | This interprets subclinical hyperthyroidism. It often happens due to Grave’s disease. |
| High | Normal | Subclinical hypothyroidism |
| Low | Normal | Subclinical hyperthyroidism |
| Normal to Low | Low | Central Hypothyroidism |
How do You Maintain a Balanced TSH level?
Now that we have covered TSH meaning, TSH normal range and value, let’s understand how we can maintain a balanced TSH level.
Having a balanced, healthy diet
The primary step to undertake in order to attain your TSH normal value is to ensure you have a healthy thyroid-friendly diet. This can include foods rich in iodine, zinc and selenium, such as seafood, sunflower seeds, nuts, eggs, dairy products and other proteins. Try to add starchy foods such as potatoes or rice.
Managing stress
Stress can lead to raised cortisol levels that can cause thyroid problems. So, ensure that you take steps to manage and reduce your stress. It can include meditation, yoga or breathing exercises.
Reducing environmental toxins
Controlling toxic habits like smoking will be effective in regulating your TSH levels. Additionally, other environmental pollutants like chemicals and metals might also interfere with your thyroid functioning. Even though these factors are out of your reach, try to avoid them as it can help you achieve your TSH normal range.
Getting enough sleep
Getting quality and sufficient sleep can improve your hormone production and the regulation of metabolism. This maintains your overall health, including thyroid functioning. So, try to get around 8 hours of sleep daily for better thyroid health.
Regular exercise
Just like getting enough sleep, having regular exercise is important for hormone and metabolism regulation and improving your thyroid health.
Monitoring Iodine intake
As we discussed earlier, iodine plays an important part in attaining the TSH normal range. But it is important to understand that taking excessive iodine can also imbalance thyroid-stimulating hormone. This makes it crucial to monitor your iodine intake.
Monitoring medications
Just like iodine intake, you need to check on your medications as well. Too many supplements for your thyroid can also be harmful. So being mindful is better.
Get regular checkups
Lastly, getting prior TSH checkups is best for early detection of any thyroid related issues. As we discussed earlier, in case you notice any of the shared symptoms, do not ignore them. Consult a medical professional for a proper diagnosis.
Conclusion
Understanding TSH levels is key to maintaining thyroid health and overall well-being. In this blog, we covered what TSH is, how high or low levels impact the body, different symptoms for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, their causes, the short test guide, and some tips to maintain a balanced TSH level. Thyroid dysfunction can affect metabolism, energy levels, and mood. Thus, it becomes important to know the symptoms of the disease and seek medical advice without delay. To achieve the TSH normal range, a well-balanced diet, regular exercise, proper medication, and stress management can help. Through crowd funding India, communities come together to help individuals manage lifelong conditions like thyroid imbalance, ensuring regular tests and proper treatment are never delayed. Your health is in your hands; do not ignore it, stay informed, take proactive measures, and prioritize your well-being.
FAQs Related to TSH Normal Range
A high TSH level indicates an underactive thyroid which is also known as hypothyroidism. It indicates that the thyroid is not producing enough hormones and to compensate for that, the pituitary gland is releasing high levels of TSH. This can lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, slow metabolism, cold intolerance and slowed metabolism.
TSH levels can be reduced by treating hypothyroidism, which is usually the cause of high TSH. Treating this involves taking thyroid hormone replacement therapy like levothyroxine, a balanced diet and regular exercise. By taking these proactive steps you can ensure having TSH normal value in your blood.
Yes, both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can lead to hair loss due to hormonal imbalances. Thyroid hormones regulate hair growth cycles and an imbalance can disturb this cycle, leading to hair thinning and excessive hair loss. In both cases, hair regrowth can be attained if you achieve the TSH normal range. Remember to take nutrient-rich diets as nutrient deficiency can worsen thyroid-related hair loss.
Yes, pregnancy significantly impacts TSH levels due to increased demands for thyroid hormones to support the growing baby. But at the same time, it’s important to know that the TSH levels are often lower than usual in the first trimester. If TSH is too high (hypothyroidism), it can lead to complications like miscarriage, preterm birth, or development issues in the baby. If TSH is too low it can again cause complications like preterm labor, high blood pressure, and other complications.
The frequency of your TSH testing depends on your health status. For those who do not have any thyroid-related issues, they can have a TSH test in a few years as a part of routine checkups. Those who are diagnosed with thyroid issues, need to take a TSH test every 6 to 12 months to monitor their thyroid levels and take measures to get their TSH normal value. During pregnancy, you need to monitor your TSH regularly to check on your thyroid health. Additionally, if you notice symptoms like fatigue, sudden weight gain or loss, or hair loss, do not ignore it and get yourself checked.
For females, the normal TSH range lies between 0.4 to 4.0 mlU/L. This depends upon factors like age, pregnancy status, menopause, or existing thyroid conditions.
The TSH normal value for men typically ranges from 0.4 to 4.0 mlU/L similar to women. However, factors such as age, lifestyle, and medical conditions can influence the range. Older men naturally have slightly higher TSH levels than young males.












