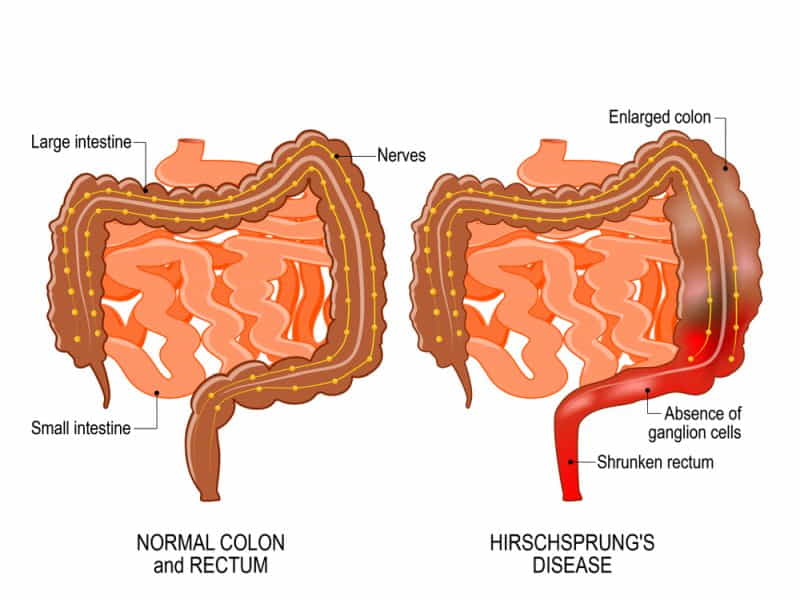
hirschsprung disease, a congenital disorder affecting the colon, poses unique challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. This condition is characterised by the absence of nerve cells in the lower part of the large intestine, impeding the regular muscle contractions necessary for bowel movements. As a result, individuals with Hirschsprung’s disease often experience difficulty passing stool, leading to various symptoms that necessitate prompt medical attention.
Symptoms of Hirschsprung’s disease typically manifest in the first few weeks of an infant’s life. Common indicators include chronic constipation, abdominal distension, vomiting, and difficulty feeding. While these symptoms may overlap with other gastrointestinal issues, healthcare professionals must consider Hirschsprung’s disease as a potential diagnosis, especially in cases where traditional interventions for constipation prove ineffective.
Treatment strategies for Hirschsprung’s disease primarily involve surgical intervention. The standard procedure, known as a pull-through surgery, aims to remove the segment of the colon lacking nerve cells and reconnect the healthy portion to the anus. The timing of surgery is based on the severity of symptoms & the overall patient’s health. In some cases, a staged approach may be adopted, with the initial surgery followed by a second procedure to optimise outcomes.
Post-surgery, individuals with Hirschsprung’s disease may experience improved bowel function, but long-term management is crucial. Dietary adjustments, medications, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are integral to ongoing care. Moreover, a supportive network involving parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals is vital to ensure the well-being of individuals living with Hirschsprung’s disease. In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of this condition, from its symptoms and diagnosis to its causes & treatment options, is essential for effective management & improved quality of life for affected patients.
Also Read: Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Causes, Symptoms, & Management
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Contrast Enema in Colon Imaging
- Hirschsprung Disease Treatment
- Hirschsprung Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment – Why It’s More Common in Males
- Hirschsprung Disease Definition & Its Types
- Hirschsprung Disease Symptoms
- Hirschsprung Disease Diagnosis
- Hirschsprung Disease Causes
- Hirschsprung Disease Life Expectancy
- Hirschsprung Disease Surgery Cost In India
- Risk Factors Of Hirschsprung Disease
- Complications Of Hirschsprung’s Disease
- Conclusion
Understanding the Role of Contrast Enema in Colon Imaging
A contrast enema is a diagnostic imaging procedure used primarily to evaluate problems in the colon and rectum. During the procedure, a contrast material—usually barium or a water-soluble iodine-based solution—is introduced into the colon through the rectum. This material outlines the inner walls of the bowel, allowing radiologists to detect abnormalities such as blockages, strictures, diverticula, or signs of diseases like Hirschsprung’s disease in children. The contrast enema is especially helpful in identifying structural changes or issues that might not be visible through other imaging methods, providing a clear view of the large intestine’s shape and condition.
A rectal biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue is taken from the rectum for examination under a microscope. This diagnostic test is often recommended when there are signs of abnormal rectal function, unexplained bleeding, chronic diarrhea, or suspicion of conditions like Hirschsprung’s disease or rectal cancer. The procedure can be performed using a sigmoidoscope or during a colonoscopy, typically under local anesthesia. By analyzing the tissue, doctors can detect inflammation, infections, abnormal nerve cells, or malignancies, allowing for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning. Though minimally invasive, a rectal biopsy plays a crucial role in identifying serious gastrointestinal conditions early.
Hirschsprung Disease Treatment
The primary treatment for Hirschsprung’s is surgery to remove the part of the colon that lacks nerve cells and reconnect the healthy part to the anus. This usually allows stool to pass through the digestive tract. Different types of surgery can be done based on the extent of the disease and the age, and the health of the patient. Some of the common surgical procedures are:
– Pull-through procedure:
This is the most common type of surgery for Hirschsprung. The surgeon eliminates the affected part of the colon & pulls the healthy part through the colon from the inside, and attaches it to the anus. This can be done using small incisions in the abdomen (laparoscopic surgery) or through the anus (transanal surgery).
– Ostomy surgery:
This is sometimes done before or instead of a pull-through procedure, especially if the patient has complications such as severe infection, megacolon, or perforation. The physician creates an opening (stoma) in the abdomen and connects it to the large or small intestine. The stool then leaves the body through the stoma into a bag connected to the intestine’s end. The stoma can be temporary or permanent, depending on whether a pull-through procedure can be done later.
– Bowel resection with colostomy:
This is another option for patients with a large portion of their colon affected by Hirschsprung disease. The surgeon removes most or all of the colon and connects the small intestine to an opening (colostomy) in the abdomen. The stool then leaves the body through the colostomy into a bag that attaches to the end of the intestine. The colostomy is usually permanent.
After surgery, most patients can pass stool through their anus and have a normal quality of life. However, some patients may have complications or ongoing problems, such as:
– Diarrhea
– Constipation
– Leaking stool (fecal incontinence)
– Delays in toilet training
– Infection and inflammation of the intestine (enterocolitis)
– Failure to thrive
These problems may improve over time with proper care and guidance from your doctor. You may need to follow a special diet, take medications, or use enemas or laxatives to manage your bowel function. You may also need regular follow-up visits and tests to monitor your condition.
If you or your child has Hirschsprung disease, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible if you notice any signs of enterocolitis, such as:
– Bleeding from the rectum
– Fever
– Swollen abdomen
– Vomiting
– Diarrhea
Enterocolitis can be life-threatening & requires immediate treatment with antibiotics and fluids. Hirschsprung disease is a severe but treatable condition that affects the colon. Most patients can have normal bowel function & quality of life with proper diagnosis and treatment.
Hirschsprung Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment – Why It’s More Common in Males
Hirschsprung disease is a rare condition, but it is four times more common in males than in females. This congenital disorder affects the large intestine and is caused by missing nerve cells in the muscles of the colon, which leads to problems with passing stool. Symptoms often appear shortly after birth and may include a swollen belly, vomiting, constipation, and failure to pass meconium within the first 48 hours of life. Early diagnosis is crucial and is typically confirmed through a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and a biopsy of the colon. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the affected portion of the intestine. Understanding why the condition is more common in males continues to be an area of research, shedding light on the complex genetic and developmental factors involved.
Hirschsprung Disease Definition & Its Types
Hirschsprung’s disease (congenital aganglionic megacolon) is a rare medical ailment that affects the large intestine (colon) & results in problems with bowel movements. The disease is present at birth and is characterised by the absence of nerve cells (ganglion cells) in the lower part of the colon. These nerve cells coordinate the muscle contractions that move stool through the intestines.
In individuals with Hirschsprung disease, the lack of ganglion cells in the affected part of the colon causes a blockage, leading to the accumulation of stool. This can result in constipation, abdominal distension, and difficulty passing stools.
There are several types of Hirschsprung based on the length of the colon affected:
1. Short-segment Hirschsprung disease:
This is the most common type, where the aganglionic segment is limited to the rectum and sometimes the sigmoid colon.
2. Long-segment Hirschsprung disease:
In this type, the absence of ganglion cells extends beyond the rectum and sigmoid colon, often involving a more significant portion of the colon.
3. Total colonic aganglionosis:
This is the most severe form, where the entire colon lacks ganglion cells.
This disease can occur as an isolated condition or be associated with other congenital disorders, such as Down syndrome or certain genetic syndromes. Early diagnosis & intervention are crucial for managing this disease and preventing complications. Many individuals with Hirschsprung disease can lead healthy and normal lives with appropriate treatment.
Hirschsprung Disease Symptoms
Symptoms of Hirschsprung disease can differ based on the severity of the condition, but common signs & symptoms include:
1. Failure to Pass Meconium:
Meconium is the thick, dark green substance that makes up a newborn’s first bowel movements. Babies with Hirschsprung may fail to pass meconium within 24 to 48 hours after childbirth.
2. Chronic Constipation:
As the child grows older, chronic constipation is a prominent symptom. The affected individual may have difficulty passing stool, which may be complicated and pellet-like.
3. Abdominal Distension:
The abdomen may become swollen or distended due to a buildup of stool in the affected area of the colon.
4. Vomiting:
Some individuals with Hirschsprung disease may experience vomiting, especially if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
5. Delayed Growth:
Chronic constipation and difficulty with regular bowel movements can lead to poor weight gain & delayed growth in infants and children.
6. Diarrhea in Newborns: In some cases, newborns with Hirschsprung disease may experience diarrhoea instead of constipation, which can be a less common presentation.
It’s vital to note that symptoms can vary, and some individuals may have milder forms of the condition. If you suspect your child may have Hirschsprung or if you are experiencing symptoms, it’s essential to contact a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Hirschsprung Disease Diagnosis
Hirschsprung disease is most often diagnosed in newborns or infants, but sometimes, it can be detected later in childhood or adulthood.
If you or your child has signs or symptoms of this disease, such as constipation, bloating, diarrhoea, fever, or blood in the stool, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. The physician will conduct a physical exam & ask about your medical and family history. They may also order one or more of the following tests to confirm or rule out Hirschsprung:
– Biopsy:
This is the most definitive test for Hirschsprung disease. It involves taking a small tissue sample from the rectum and examining it under a microscope to look for the presence or absence of nerve cells. A biopsy can be done using a suction device inserted through the anus or by cutting out a small piece of tissue during surgery.
– Barium enema:
This X-ray test uses a contrast dye to show the outline of the colon. The dye is inserted into the bowel through a tube in the rectum. The X-ray will show if there is a narrow section of the bowel without nerves and a swollen section behind it.
– Anal manometry:
This is a test that measures the pressure and relaxation of the muscles around the rectum. It is usually done on older children and adults. A balloon is inflated inside the rectum, and the doctor observes how the muscles react. If they do not relax, it may indicate Hirschsprung disease.
Hirschsprung Disease Causes
The primary cause of Hirschsprung’s disease is the absence of nerve cells (ganglion cells) in the lower part of the colon.
In a typical digestive system, the muscles in the walls of the colon coordinate contractions to move stool through the intestines. Nerve cells, particularly the ganglion cells, play a crucial role in regulating these contractions. In individuals with Hirschsprung’s disease, the nerve cells are missing from a segment of the colon, usually the rectum and part of the sigmoid colon. This absence of ganglion cells leads to a lack of coordinated contractions in the affected segment, causing a functional obstruction.
The precise cause of the absence of ganglion cells in Hirschsprung’s disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a result of abnormal development of the enteric nervous system during fetal development. The enteric nervous system is a complex chain of nerves within the borders of the gastrointestinal tract that controls various digestive functions.
There are a few factors and conditions that may contribute to the development of Hirschsprung’s disease:
1. Genetic Factors:
Hirschsprung’s disease can run in families, and there is evidence of a genetic predisposition. Mutations in several genes have been determined as associated with this medical condition. The RET gene, in particular, is known to play a crucial role in the development of the enteric nervous system.
2. Embryonic Development:
The absence of ganglion cells is thought to occur during embryonic development when neural crest cells, which give rise to different cell types in the body, fail to migrate and colonise the lower part of the colon properly.
3. Environmental Factors:
While the primary cause is genetic, certain environmental factors may influence the development of Hirschsprung’s disease. These factors could include issues during pregnancy, such as maternal smoking.
4. Associated Syndromes:
In some cases, Hirschsprung’s disease may be associated with other genetic syndromes, such as Down syndrome and Waardenburg syndrome.
It’s important to note that Hirschsprung’s disease is a congenital medical condition, meaning it is present at birth. The symptoms usually become apparent in the first few weeks of life, and diagnosis and treatment typically follow soon after.
Hirschsprung Disease Life Expectancy
According to some sources, about 5% of children with this disease still die of this disorder, typically as a result of enterocolitis. However, the risk of death is dramatically reduced once the disease is recognised and treated. Most people with Hirschsprung disease have an average life expectancy after treatment. However, they may still face some challenges or complications that require lifelong care and monitoring.
The prognosis and outlook for patients with HD depend on several factors, such as the age at diagnosis, the length of the affected bowel, the presence of complications, and the quality of surgical and postoperative care. Advances in surgical techniques & perioperative care have improved the short- and mid-term outcomes of patients with HD. Still, the long-term outcomes (older than 10 years) have yet to be thoroughly investigated.
As per a systematic review & meta-analysis of 12 studies that included 625 patients with HD older than 10 years, the pooled prevalences of faecal incontinence, constipation, and bladder dysfunction symptoms were 0.20 (95% CI 0.13–0.28), 0.14 (95% CI 0.06–0.25), and 0.07 (95% CI 0.04–0.12), respectively; the pooled mean score of gastrointestinal-related quality of life was 118 (95% CI: 112.56–123.44). These results indicate that HD patients older than 10 years have an overall high prevalence of faecal incontinence and low quality of life.
Hirschsprung Disease Surgery Cost In India
The average cost of this disease surgery in India ranges from INR 1,50,000 to INR 3,00,000. However, this is only an approximate figure and may differ from one hospital to another. Therefore, it is advisable to contact the hospital directly and get a personalised quote based on your specific case.
Some of the best hospitals in India that offer Hirschsprung disease surgery are:
– Gleneagles Global Hospitals in Chennai
– BLK Super Speciality Hospital in Delhi
– Apollo Hospitals in Chennai
– Fortis Hospital in Gurgaon
– Artemis Hospitals in Gurgaon
These hospitals are accredited by national and international organisations such as NABH, JCI, and ISO. They have experienced surgeons who specialise in pediatric surgery and colorectal surgery. They also have advanced equipment and facilities to ensure a safe & successful outcome for the patients.
Risk Factors Of Hirschsprung Disease
While the exact cause of Hirschsprung disease is not well understood, several risk factors have been identified. It’s important to note that these factors may increase the likelihood of developing the condition but do not guarantee it. The primary risk factors associated with Hirschsprung include:
1. Genetics:
– Hirschsprung disease often has a genetic component. Mutations in certain genes, such as the RET gene, have been linked to the development of HD. The RET gene plays a vital role in the development of the enteric nervous system, and mutations can disrupt the normal formation of nerve cells in the intestine.
2. Family History:
– Individuals with a family history of Hirschsprung disease are at a higher risk of developing the medical condition. If a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, has HD, the likelihood of inheriting the genetic predisposition may be higher.
3. Gender:
– Hirschsprung disease is more common in males than in females. The reason for this gender difference is not entirely understood, but it suggests that there may be hormonal or genetic factors influencing the development of the disorder.
4. Congenital Conditions:
– HD is sometimes associated with other congenital conditions, such as Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. Individuals with certain congenital disorders may have an increased risk of developing Hirschsprung disease.
5. Prematurity:
– Babies born prematurely are at a slightly higher risk of developing Hirschsprung disease. The reasons for this association are unclear, but it may be related to premature infants’ incomplete development of the enteric nervous system.
6. Maternal Smoking:
– Some studies suggest a possible association between maternal smoking during pregnancy & an increased risk of Hirschsprung disease in offspring. However, more research is needed to establish a definitive link.
7. Other Environmental Factors:
– There is ongoing research to explore potential environmental factors that may contribute to the development of Hirschsprung disease. However, at present, specific environmental influences still need to be well-established.
It’s essential to recognise that while these risk factors may increase the likelihood of Hirschsprung disease, the majority of cases happen sporadically without a clear family history or identifiable risk factor. Genetic counselling can be beneficial for families with a history of HD or individuals with concerns about the risk of passing the condition to their children.
Complications Of Hirschsprung’s Disease
While surgery is the primary treatment for Hirschsprung disease, complications can arise before and after the surgical intervention. Here are some of the potential complications associated with this disease:
1. Enterocolitis:
– Description: Enterocolitis is a severe complication that can occur in individuals with Hirschsprung. It involves inflammation of the colon & small intestine and can lead to severe abdominal pain, fever, diarrhoea, and vomiting.
– Cause: The absence of ganglion cells in the affected segment of the colon impairs normal bowel movements and can lead to the accumulation of stool, causing bacterial overgrowth. This, in turn, increases the risk of infection and inflammation.
2. Bowel Obstruction:
– Description: Due to the lack of coordinated muscle contractions in the affected segment of the colon, there is a risk of bowel obstruction.
– Cause: The accumulation of stool in the colon can lead to a blockage, causing abdominal pain, distension, and vomiting.
3. Failure to Thrive:
– Description: Children with Hirschsprung disease may experience difficulty gaining weight and growing at a regular rate.
– Cause: The functional obstruction of the colon can lead to chronic constipation and feeding difficulties, contributing to poor nutritional intake.
4. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders:
– Description: Some individuals may experience ongoing bowel function and motility issues after surgery.
– Cause: Surgical procedures to remove the aganglionic segment can sometimes result in long-term alterations to bowel motility.
5. Anorectal Dysfunction:
– Description: Some patients may experience problems with the anal sphincter and rectum, leading to difficulty controlling bowel movements.
– Cause: Surgical procedures may affect the normal function of the anal sphincter.
6. Scar Tissue Formation:
– Description: Surgical interventions can lead to scar tissue formation, which may cause strictures or narrowing in the affected area.
– Cause: Healing after surgery can result in the formation of fibrous tissue, potentially causing complications.
It’s important to note that early diagnosis and appropriate management, often involving surgical correction, can significantly improve outcomes & reduce the risk of complications associated with Hirschsprung disease. Regular follow-up care & monitoring are essential to address any potential issues that may arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hirschsprung disease is a rare but significant congenital condition that affects the large intestine, leading to complications in bowel movements. Recognising symptoms that often manifest in infancy is crucial for an early diagnosis. The primary cause of the disease is the absence of nerve cells in the lower part of the colon, hindering the normal movement of stool. Diagnosis involves medical history assessment, physical examination, and various imaging studies.
Treatment options for this disease typically involve surgery to extract the affected part of the colon and reconnect the healthy segments. Postoperative care and management may include dietary adjustments and medications to address residual issues. While the condition poses challenges, early intervention & proper medical care can considerably improve the quality of life for individuals with Hirschsprung.
rectal biopsyThe support of a multidisciplinary healthcare team, including pediatric surgeons, gastroenterologists, and specialised nurses, is essential for comprehensive care. Ongoing research & advancements in medical science continue to improve understanding and treatment strategies for Hirschsprung disease, offering hope for better outcomes & a brighter future for affected individuals and their families.
Hirschsprung Disease surgery often entails significant medical expenses, including pre-operative assessments, the surgery itself, post-operative care, and potential complications. A fundraising platform offers a practical solution to alleviate the financial burden on affected families, ensuring that cost is not a barrier to life-saving treatment. The platform creates a space for friends, family, and compassionate individuals to come together and support those facing the challenges of this Disease. Crowdfunding helps you reach out for financial assistance for your healthcare.












