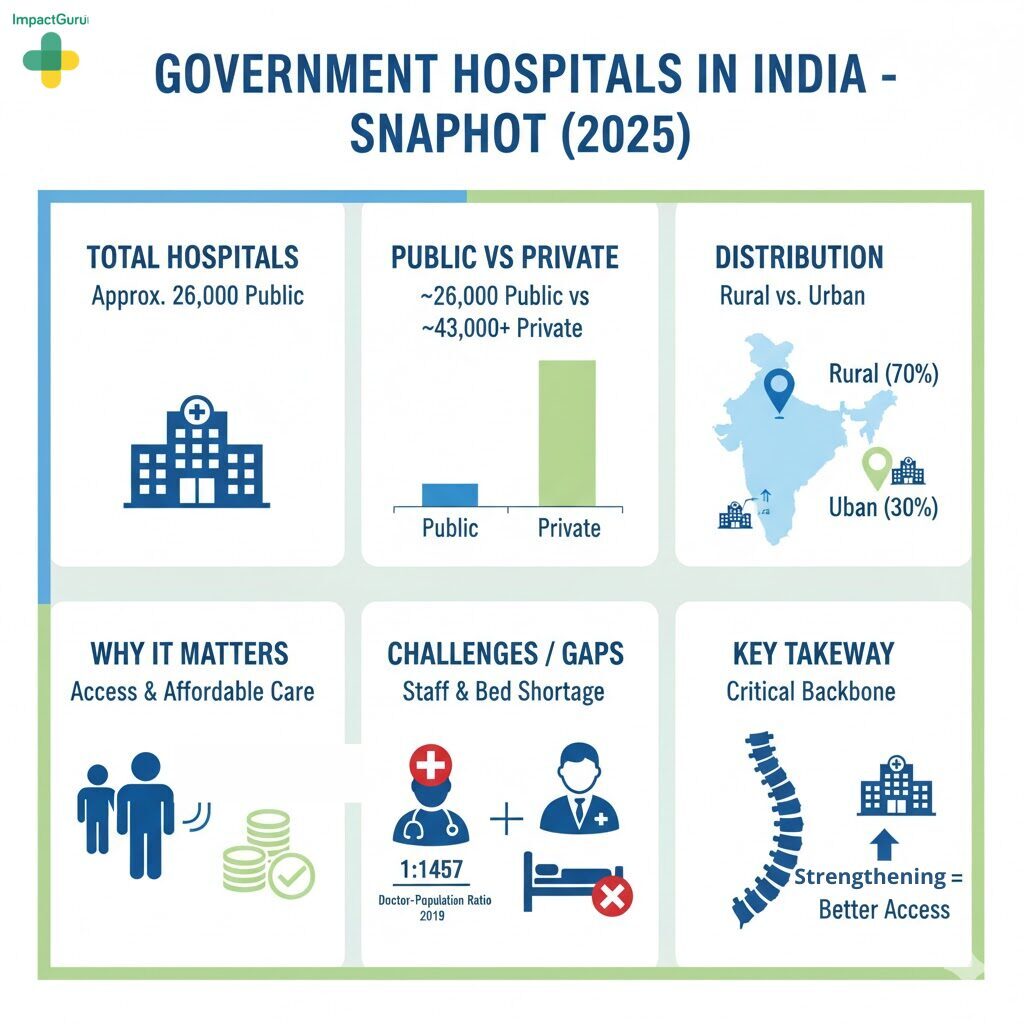
India’s healthcare system is one of the largest in the world, serving over a billion people across urban and rural regions. At the core of this large system lie the government hospitals in India, which provide affordable and accessible treatment for millions.
These hospitals are critical in ensuring that healthcare reaches every corner of the country, regardless of income or location. Government hospitals in India provide affordable healthcare and advanced treatment options for millions of patients. However, for additional expenses like medicines or specialized procedures, crowdfunding in India can help patients bridge the gap.
Unlike private hospitals, which can be expensive, Indian government hospitals aim to provide equal care to all. From basic patient consultations to life-saving surgeries and specialty treatments, they offer a wide range of free or subsidized services.

This makes them important for the country’s public health goals. Even with subsidized treatment, some families may face financial challenges. Patients can
raise money online to cover extra costs, ensuring timely access to surgeries, diagnostics, and medications.
As the need for quality healthcare continues to rise, understanding the structure, scale, and significance of government hospitals becomes essential. In this guide, we will explore how many government hospitals in India exist, their distribution, and a list of govt hospitals in India ranked based on their services, infrastructure, capacity, and more.
We will also look at how the system works, from registration to treatment, challenges faced by public hospitals, and how ongoing reforms are shaping the future of healthcare in India. Trusted crowdfunding platforms allow patients to share their medical journey and reach donors who are willing to contribute toward treatment in government hospitals, making healthcare more accessible.
Click here to read about Best Government hospitals in Mumbai.
Read More: Benefits of Organ Donation: Criteria & Registration Process
Table of Contents
Structure of the Indian Government Hospital System

The Indian government hospital system is organized into multiple levels, ensuring healthcare access for every citizen. This system is largely divided into Central, State, and Local hospital networks and operates across three levels of care: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary. Additionally, various government medical colleges and healthcare schemes strengthen the public infrastructure. Here is a brief account of them:
Read More : How to Become a Kidney Transplant Donor In India?
Click Here to Find Best Hospitals Near You
While treatment at government hospitals can significantly reduce medical costs, having a reliable health insurance plan through platforms like Carepal Secure ensures better financial protection during critical care.
A. Types of Government Hospitals in India
1. Central Government Hospitals
Central government hospitals, as the name suggests, are operated and funded by the central government. They are directly managed and operated by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, often offering highly specialized care and medical education.
With increasing healthcare demands, crowdfunding India has emerged as a reliable support system for patients seeking affordable care and additional medical resources in government hospitals.
Some of the examples of Central government hospitals in India are AIIMS (New Delhi and branches), Safdarjung Hospital, PGIMER Chandigarh, and RML Hospital. Using a secure crowdfunding platform in India ensures transparency, faster fund transfers, and a wider donor reach, helping patients meet their healthcare needs effectively.
2. State Government Hospitals
The state health departments administer these hospitals. They form the bulk of public healthcare services, covering district, taluk, and specialty hospitals.
Examples of state government hospitals in India include Rajiv Gandhi Government General Hospital (Chennai), KEM Hospital (Maharashtra), and District General Hospitals.
3. Municipal or Local Body Hospitals
Local body hospitals are healthcare facilities managed by local bodies like municipal corporations or city councils. These hospitals serve densely populated urban areas and provide essential services at affordable costs.
Examples of municipal hospitals include Lokmanya Tilak Municipal General Hospital (Mumbai), Sion Hospital.
Read More: Liver Transplant Waiting List: Registration & Criteria
B. Levels of Care in Government Hospitals
1. Primary Healthcare
Primary healthcare is the first point of contact between individuals and the healthcare system, as it focuses on preventive, promotive, and basic curative services, especially in rural and underserved areas.
Facilities Provided:
- Health education and awareness
- Immunization programs
- Maternal and child care
- Family planning
- Treatment of common illnesses
2. Secondary Healthcare
Secondary healthcare provides specialist care through district and sub-divisional hospitals and serves as a referral point from PHCs and CHCs. It bridges the gap between basic and super-specialty care.
Facilities Provided:
- Inpatient care and minor surgeries
- Specialist consultations (pediatrics, OB-GYN, general medicine)
- Emergency services
3. Tertiary Healthcare
Tertiary healthcare provides the highest level of medical treatment. It involves advanced treatment for complex illnesses and super-specialty services. Additionally, these institutions are often linked to teaching and research.
Facilities Provided:
- Organ transplants, cancer treatment, and neurosurgery
- Medical research and education
- Super-specialty clinics
- Read More: Liver Size Normal Range and Health Indicator
C. Government Medical Colleges and Teaching Hospitals
Government medical colleges and their attached hospitals play a dual role of providing high-quality medical education and delivering specialized healthcare services. These teaching hospitals are very important for training India’s next generation of doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals while also functioning as tertiary referral centers for complex and critical medical cases.
Examples of Government Teaching Hospitals in India:
- AIIMS (Delhi and regional branches)
- Madras Medical College
- KEM Hospital (Mumbai)
- Government Medical College, Kozhikode
These institutions play an important role in developing India’s healthcare workforce while delivering top care.
Read More: Guide to Body Parts Donation in India
Read More: Liver Transplant Donor Criteria: Complete Guide for India
D. Public Healthcare Schemes Supporting Government Hospitals
India’s public healthcare system is supported by several government-funded schemes that aim at ensuring health coverage, especially for the underprivileged. These schemes support government hospitals in delivering free or subsidized medical services. Here are some of them:
1. Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
PM-JAY was started in 2018 and is the world’s largest health assurance scheme, covering over 50 crore individuals. It provides cashless and paperless hospitalization for secondary and tertiary care. It offers coverage of up to Rs. 5 lakh per family per year.
2. Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS)
CGHS targets central government employees, pensioners, and their dependents. It offers access to dispensaries, wellness centers, polyclinics, and government referral hospitals. This scheme is available in cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, and is expanding gradually.
3. Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESI)
ESI is managed by ESIC and supports workers in the organized sector and their families. It is funded through employer and employee contributions. This scheme provides complete medical care, including hospitalization in ESIC or empaneled government hospitals.
4. Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN
RAN provides financial assistance for catastrophic diseases like cancer, kidney/liver transplants for families below the poverty line (BPL). Treatments under this scheme are offered at super-specialty government hospitals, including AIIMS and regional institutions.
5. State-Specific Health Schemes
Many Indian states have started their health protection schemes that integrate with or complement national programs: Aarogyasri (Telangana & Andhra Pradesh) offers free tertiary care for BPL families. Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Jan Arogya Yojana (Maharashtra) covers surgeries and treatment for low-income groups. Karunya Health Scheme (Kerala) covers the cost of major treatments in public hospitals. Biju Swasthya Kalyan Yojana (Odisha) offers cashless healthcare at state and central government hospitals.
Impact of These Schemes:
These schemes encourage the utilization of government hospitals over private ones. It reduces expenditure for poor and middle-income families. It also adds to the investments in infrastructure and digital health records in public health systems. Additionally, these schemes promote public-private partnerships (PPP) while strengthening the core government framework.
Click Here To Know More about Best Government Hospitals in India
1. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi
Hospital Name: All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi
Headed by: Dr. M. Srinivas (Director, AIIMS New Delhi)
Operational days: Monday to Saturday
Establishment: 1956
Founder: Government of India (established under an Act of Parliament)
Number of Beds: Approximately 2,500 beds
Address: Ansari Nagar, New Delhi, Delhi – 110029, India
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, established in 1956, is India’s top-ranked government medical institute offering advanced healthcare, education, and research under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Located in South Delhi, AIIMS provides affordable and comprehensive medical services across 50+ specialties, including cardiology, oncology, neurology, and orthopaedics. With over 2,500 beds and modern diagnostic technology, the hospital serves millions of patients annually from across India and abroad. As a national center of excellence, AIIMS combines patient care, medical innovation, and academic leadership, setting benchmarks in India’s healthcare system.
2. Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER)
Hospital Name: Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh
Headed by: Prof. Vivek Lal (Director, PGIMER)
Operational days: Monday to Saturday
Establishment: 1962
Founder: Government of India
Number of Beds: Approximately 2,000 beds
Address: Sector 12, Chandigarh – 160012, India
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, established in 1962, is one of India’s leading government-run tertiary care hospitals and academic institutions. Operating under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, PGIMER is renowned for its medical education, advanced research, and comprehensive patient care.
The institute provides high-quality and affordable treatment in over 50 medical specialties, including cardiology, neurology, nephrology, oncology, and gastroenterology. With around 2,000 beds and state-of-the-art facilities, PGIMER attracts patients from all parts of India seeking specialized healthcare and compassionate service.
3. Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research (JIPMER)
Hospital Name: Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research (JIPMER), Puducherry
Headed by: Prof. Rakesh Aggarwal (Director, JIPMER)
Operational days: Monday to Saturday
Establishment: 1964
Founder: Government of India
Number of Beds: Approximately 2,000 beds
Address: Dhanvantari Nagar, Gorimedu, Puducherry – 605006, India
Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research (JIPMER), Puducherry, established in 1964, is a premier government medical institution offering integrated healthcare, education, and research. Operated under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, JIPMER provides affordable and high-quality medical care to patients from across India.
The institute specializes in multiple fields including cardiology, oncology, neurology, nephrology, and surgery, supported by modern medical technology and expert doctors. With around 2,000 beds and advanced treatment facilities, JIPMER stands as one of the most trusted public hospitals in South India, known for its compassionate patient care and academic excellence.
4. Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS)
Headed by: Prof. R. K. Dhiman (Director, SGPGIMS)
Operational days: Monday to Saturday
Establishment: 1983
Founder: Government of Uttar Pradesh
Number of Beds: Approximately 1,000 beds
Address: Raebareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh – 226014, India
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS), established in 1983 in Lucknow, is a leading government medical institute specializing in postgraduate medical education, research, and advanced patient care. Operating under the Government of Uttar Pradesh, SGPGIMS offers specialized healthcare in fields such as cardiology, nephrology, neurology, endocrinology, and gastroenterology.
With modern diagnostic facilities and around 1,000 beds, the institute serves as a referral center for complex medical cases across North India. Known for its academic excellence and clinical expertise, SGPGIMS continues to play a vital role in advancing healthcare standards in India.
5. King Edward Memorial (KEM) Hospital, Mumbai
Headed by: Dr. Hemant Deshmukh (Dean, KEM Hospital & GSMC)
Operational days: Monday to Saturday
Establishment: 1926
Founder: Established under the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai, affiliated with Seth G.S. Medical College
Number of Beds: Approximately 1,800 beds
Address: Acharya Donde Marg, Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400012, India
King Edward Memorial (KEM) Hospital, founded in 1926 in association with Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College, is one of India’s oldest and most respected government hospitals. Located in Parel, Mumbai, KEM Hospital provides comprehensive healthcare services to patients from Maharashtra and across the country.
With nearly 1,800 beds and a highly experienced medical team, it offers advanced care in cardiology, orthopaedics, oncology, neurology, and general medicine. Known for its medical education, affordable treatment, and social outreach, KEM remains a cornerstone of public healthcare in Western India.
6. Tata Memorial Hospital
Headed by: Dr. Sudeep Gupta (Director, Tata Memorial Centre)
Operational days: Monday to Saturday
Establishment: 1941
Founder: Sir Dorabji Tata Trust (now managed by Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India)
Number of Beds: Approximately 700 beds
Address: Dr. Ernest Borges Road, Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400012, India
Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), Mumbai, established in 1941, is India’s foremost government-run cancer hospital dedicated to comprehensive oncology care, research, and education. Operated by the Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India, TMH provides world-class cancer diagnosis and treatment at affordable costs.
With around 700 beds and advanced radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgical oncology units, it serves thousands of patients every year from India and abroad. The hospital is part of the Tata Memorial Centre network, which integrates treatment, training, and cancer research to advance oncology care nationwide.

Click Here To Get an Estimate Cost For Your Disease Treatment
Easily refer a patient for medical help and treatment assistance online.
FAQs
As of recent data from the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India has over 23,581 government hospitals, including primary health centres (PHCs), community health centres (CHCs), district hospitals, and tertiary care institutions like AIIMS and state medical colleges. These hospitals serve urban, semi-urban, and rural populations across the country.
Yes, most government hospitals in India provide free healthcare services, especially for basic consultations, emergency treatment, and essential medicines. Advanced procedures or private room preferences may involve minimal charges. Additionally, schemes like Ayushman Bharat (PM-JAY) offer free treatment up to ₹5 lakhs annually for eligible families at many government hospitals.
Government hospitals in India offer several advantages, including affordable or free treatment for all sections of society, wide coverage, especially in rural and underserved areas. Availability of specialists in major hospitals, access to national health schemes like Ayushman Bharat, and tertiary care and teaching hospitals that offer advanced treatment and training
Delhi is often considered to have the best government hospitals, with AIIMS Delhi leading the list for its excellent infrastructure, medical research, and quality care. States like Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka also have high-quality government hospitals such as KEM Hospital (Mumbai), RGGGH (Chennai), and Victoria Hospital (Bangalore), respectively.
Government hospitals in India often provide a wide spectrum of care, ranging from primary services (like general consultations, immunizations and maternal‑child health) to secondary care (district/sub‑divisional hospitals for specialist consultations, surgeries, diagnostics) and even tertiary or super‑specialty treatments (such as organ transplants, advanced cancer treatment, neurosurgery, medical research and teaching) in major government institutions.












