Fibroadenoma, a term often heard in the realm of breast health, is a non-cancerous and generally benign tumor that commonly affects women, especially those in their reproductive years. As one of the most prevalent breast conditions, this can raise concerns and questions about its nature, causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
This complete guide aims to shed light on various aspects of this disease, offering a comprehensive understanding of the condition to empower individuals with knowledge and facilitate informed decisions.
Firstly, it is essential to comprehend the meaning of this. The term “fibroadenoma” is derived from its composition – a combination of fibrous and glandular tissues. These tumors typically manifest as small, firm lumps in the breast, known for their smooth texture and well-defined borders. While this is generally painless, they can cause discomfort or become tender during the menstrual cycle.
The precise causes of this disease remain elusive, but hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen, are believed to play a crucial role. These tumors often develop during reproductive years when hormonal activity peaks. Genetics may also contribute to an individual’s predisposition to this, with a family history of the condition increasing the likelihood of its occurrence.
Understanding the symptoms is paramount for early detection and appropriate management. These usually present as painless, movable lumps in the breast. However, it is crucial not to rely solely on self-diagnosis. Regular breast self-exams, coupled with clinical breast examinations and imaging studies like mammograms or ultrasounds, form a comprehensive approach for accurate diagnosis.
Upon a confirmed diagnosis, treatment choice depends on various factors, including the size of the that, its characteristics, and the patient’s overall health. Many of them do not necessitate treatment and may resolve on their own. However, surgical removal may be prescribed if the disease causes discomfort, proliferates, or exhibits concerning features. Minimally invasive procedures, such as ultrasound-guided biopsy or cryoablation, are also emerging as alternative treatment options.
Beyond the physical aspects, it is crucial to address the emotional impact of a diagnosis. Anxiety and fear are common reactions, and patients benefit from open communication with healthcare professionals, support groups, and friends or family. Understanding that fibroadenomas are usually benign and not indicative of breast cancer can alleviate emotional distress.
In conclusion, navigating this realm involves understanding their meaning, causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Armed with knowledge, individuals can proactively engage in their healthcare, making informed decisions in collaboration with their healthcare providers. This blog aims to empower and reassure those facing fibroadenoma, fostering a sense of control and well-being in the face of this common breast condition.
Table of Contents
- Fibroadenoma Treatments
- Surgical treatments
- Fibroadenoma Surgery Side Effects
- Fibroadenoma Symptoms
- Understanding Breast Masses: Causes and Evaluation
- Fibroadenoma Meaning
- Finding a Breast Lump and Undergoing Multiple Surgeries
- Fibroadenoma Causes
- Fibroadenosis Vs. Fibroadenoma
- Phyllodes Tumor Vs. Fibroadenoma
- Exploring Health Information and Outreach Through Digital Platforms
- Types Of Fibroadenoma
- How To Diagnose Fibroadenoma?
- Risk Factors For Fibroadenomas
- Conclusion
Fibroadenoma Treatments
There are two main types of this disease treatment: surgical and non-surgical. Surgical treatments involve removing the tumor wholly or partially, while non-surgical treatments aim to shrink or destroy the cancer without surgery.
Surgical treatments
Surgical treatments for fibroadenoma include:
– Lumpectomy:
This is the most common surgical treatment for fibroadenoma. It involves making a small incision in the breast and removing the tumor along with a margin of normal tissue around it. The incision is then closed with stitches or glue. Lumpectomy preserves the shape and appearance of the breast and has a low risk of complications. However, it may leave a scar or cause changes in breast sensation.
– Mastectomy:
This is a rare surgical treatment for this. It involves removing the entire breast that contains the tumor. Mastectomy is usually reserved for very large or multiple tumors that cannot be removed by lumpectomy or for women who have a high risk of breast cancer. Mastectomy can cause a significant emotional and physical impact and may require breast reconstruction surgery.
Fibroadenoma Surgery Side Effects
Here are some potential side effects of fibroadenoma surgery:
1. Pain and Discomfort:
It is common to face some pain or discomfort at the surgical site after the surgery. This can be handled with the recommended pain medicines.
2. Swelling and Bruising:
Swelling & bruising around the surgical area are normal and typically subside over time.
3. Scarring:
The surgical incision will leave a scar, and its appearance can vary. The scar may be noticeable in some cases, while in others, it may fade over time.
4. Infection:
There is a possibility of acquiring an infection at the surgical site. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, and discharge. Antibiotics may be recommended to restrict or treat infections.
5. Bleeding:
Some degree of bleeding is expected during and after surgery. Excessive bleeding may require medical attention.
6. Changes in Sensation:
Some women may experience shifts in sensation around the breast or nipple area, including numbness or increased sensitivity. In most cases, these changes are temporary.
7. Wound Healing Issues:
Sometimes, wound healing may be delayed, leading to poor scar formation or wound dehiscence (wound opening). This may require additional medical attention.
8. Rare Complications:
While uncommon, there are potential rare complications, such as damage to nearby structures, nerve injury, or problems with anesthesia. Your surgeon will discuss the potential risks & benefits of the procedure with you before surgery.
Non-surgical treatments
Non-surgical treatments for this disease include:
– Cryoablation:
This is a minimally invasive treatment for the disease. It involves inserting a thin probe into the tumor and freezing it with liquid nitrogen. The frozen tissue then dies and is gradually absorbed by the body. Cryoablation does not require stitches or anesthesia and has minimal scarring and pain. However, it may not be effective for large or deep fibroadenomas and may cause infection or bleeding.
– Radiofrequency ablation:
This is another minimally invasive treatment for this disease. It involves putting a thin needle into the tumor and heating it with radio waves. The heat destroys the tumor cells and causes them to shrink.
Radiofrequency ablation does not require stitches or anesthesia and has minimal scarring and pain. However, it may not be effective for large or deep wounds and may cause infection or bleeding.
– High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU):
This is a non-invasive treatment for this. It involves using ultrasound waves to target and destroy the tumor without damaging the surrounding tissue. HIFU does not require any incision or anesthesia and has no scarring or pain. However, it may only be available in some hospitals and may take several sessions to achieve complete results.
Cost of fibroadenoma treatments in India
The cost of the treatments this disease in India depends on various factors, such as:
– The type of treatment chosen
– The size and location of the tumor
– The experience and reputation of the doctor
– The accreditation and location of the hospital
– The room category and duration of stay
– The insurance coverage and medical tourism package
The approximate cost of fibroadenoma treatments in India is as follows:
| Treatment | Cost (INR) |
| Lumpectomy | 30,000 – 60,000 |
| Mastectomy | 1,00,000 – 2,00,000 |
| Cryoablation | 50,000 – 1,00,000 |
| Radiofrequency ablation | 50,000 – 1,00,000 |
| HIFU | 1,00,000 – 2,00,000 |
These costs are only indicative and may vary from hospital to hospital & patient to patient.
Fibroadenoma Symptoms
Fibroadenomas are common benign (non-cancerous) breast tumors that primarily affect women. These tumors are composed of both glandular and connective tissue and often occur in reproductive-aged women. these are usually smooth, firm, and mobile lumps that can vary in size.
While these are typically not associated with noticeable symptoms, some women may experience certain signs related to the presence of these tumors. Here are some potential symptoms:
1. Breast Lump:
– The most common symptom of this disease is the presence of a breast lump. These lumps are usually painless, well-defined, and easily movable within the breast tissue. They often feel rubbery or firm.
2. Change in Size:
– This can change in size over time. They may grow larger or smaller, and some women may notice fluctuations in the size of the lump during their menstrual cycle.
3. Breast Pain or Tenderness:
– In some cases, this may be associated with breast pain or tenderness. However, this is not a universal symptom, and many women with that do not experience any pain.
4. Smooth Edges:
– This typically have well-defined, smooth edges. This distinguishes them from other types of breast lumps that may have irregular or jagged borders.
5. Mobile Lump:
– The lump associated with this is usually easily movable within the breast tissue. It can be shifted under the skin and is not fixed to the surrounding structures.
6. Visible Changes in the Breast:
– While rare, large fibroadenomas may cause visible differences in the shape or appearance of the breast. This is more common when the lump is close to the surface of the breast.
It’s important to note that these are generally benign, and the majority do not increase the risk of developing breast cancer. However, a medical professional should evaluate any new or unusual breast changes.
Diagnostic tools such as mammograms, ultrasound, or biopsy may be used to confirm the nature of the breast lump and rule out other potential causes. If you observe any fluxes in your breast tissue or have concerns about breast health, it’s better to seek medical attention for a thorough evaluation.
Understanding Breast Masses: Causes and Evaluation
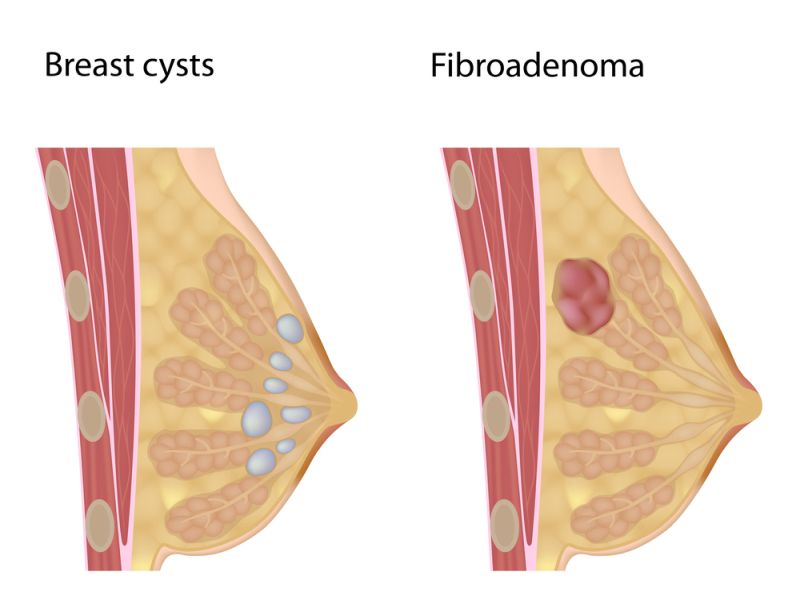
Breast masses are abnormal lumps or swellings found within breast tissue and can vary widely in size, texture, and cause. While many breast masses are benign, such as cysts or fibroadenomas, others may indicate more serious conditions, including breast cancer.
It is crucial to monitor any changes in breast masses through self-examinations and regular medical screenings to ensure early detection and appropriate treatment. Prompt evaluation of breast masses by a healthcare professional can provide peace of mind and guide necessary next steps.
Fibroadenoma Meaning
This benign (noncancerous) breast lump is made of glandular and fibrous tissues. It is one of the most common breast lumps in young women, especially between the ages of 15 and 35. It can also result during pregnancy or breastfeeding, possibly related to hormonal changes.
A fibroadenoma usually feels like a firm, smooth, rubbery lump that moves quickly under the skin. It may be round or flat, and it can differ in size from a pea to larger than 2 inches. Most of these do not cause pain or other symptoms, but some may be tender or sore before menstrual.
A fibroadenoma is not a sign of breast cancer, and it does not increase the risk of developing breast cancer. However, it is essential to see a doctor if you find a new breast lump or notice any changes in your breasts. A doctor can examine the lump and perform tests like a mammogram, ultrasound, or biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Many of these diseases do not require any treatment, as they may shrink or disappear over time. However, some of them may grow larger or cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns. A doctor may recommend removing the lump with surgery or other methods in these cases. The removal of this disease does not affect the normal function or appearance of the breast.
Fibroadenomas are benign breast lumps that are common in young women. They are not cancerous and do not pose a severe health threat. However, they should be checked by a doctor to confirm the diagnosis & monitor any changes. If you have any questions or concerns about that or your breast health, talk to your doctor or a breast specialist.
Finding a Breast Lump and Undergoing Multiple Surgeries
Finding a lump in your breast can be an alarming experience, often bringing a flood of questions and concerns. While not all lumps are cancerous, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation promptly to determine the cause. Some lumps may be benign cysts or this, but in other cases, further testing is necessary.
If a diagnosis suggests the lump is suspicious or malignant, surgery to remove it may be recommended. Early detection significantly improves outcomes, making awareness and timely action essential.
In some situations, individuals may face the challenge of undergoing surgery to remove lumps more than once. This can happen if new lumps are found over time or if the initial surgery didn’t remove all the abnormal tissue.
Experiencing surgery to remove a lump multiple times can be emotionally and physically taxing, but it is often a proactive step to ensure ongoing health. Regular follow-up appointments, imaging, and consultations with healthcare professionals help guide these decisions and support patients through the process.
Fibroadenoma Causes
While the exact cause of this disease is not well understood, there are several factors that may contribute to its development. These factors include:
1. Hormonal Influences:
Hormonal changes, particularly fluctuations in estrogen levels, are believed to play a vital role in developing this. These tumors often appear and may grow during reproductive years when estrogen levels are higher, such as during puberty, pregnancy, and the menstrual cycle.
2. Reproductive Factors:
Women who have not given birth or have delayed childbirth may have a slightly higher risk of developing fibroadenomas. Additionally, early onset of menstruation and late onset of menopause may be associated with an increased risk.
3. Genetics:
There may be a genetic predisposition to fibroadenomas. If a woman has a family history of these tumors, her risk of developing them may be higher.
4. Hormonal Medications:
Certain hormonal medications, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and oral contraceptives (birth control pills), may influence the development or growth of fibroadenomas.
5. Race and Age:
Fibroadenomas are more common in women of African heritage and women under the age of 30. However, they can occur in women of any age or race.
6. Breast Trauma:
Some studies suggest that trauma or injury to the breast may be a factor in the development of fibroadenomas. However, this is not universally accepted, and more research is needed to establish a clear connection.
Fibroadenosis Vs. Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenosis and fibroadenoma are both terms related to the breast but refer to different conditions.
1. Fibroadenosis (also known as fibrocystic breast changes or benign breast disease):
– Nature: Fibroadenosis is a non-cancerous (benign) condition.
– Description: It involves changes in the breast tissue, leading to the development of lumps or areas of thickened tissue. These changes can cause the breasts to feel lumpy or nodular.
– Symptoms: Fibroadenosis may cause breast pain, tenderness, and swelling, especially before menstruation. The lumps can be more pronounced during certain times of the menstrual cycle.
– Risk factors: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those during the menstrual cycle, may contribute to the development of fibroadenosis.
– Diagnosis: Typically diagnosed through clinical examination, imaging studies (like mammography or ultrasound), & sometimes a biopsy to rule out other conditions.
2. Fibroadenoma:
– Nature: This is also a non-cancerous (benign) tumor.
– Description: It is a solid, usually painless lump that is well-defined and mobile within the breast tissue. Fibroadenomas are composed of both glandular and connective tissue.
– Symptoms: These are often discovered by women themselves or during a clinical breast examination. They are usually not associated with breast pain, but some women may feel discomfort.
– Age: These are more common in younger women and adolescents.
– Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically confirmed through imaging studies (ultrasound, mammography) and, in some cases, a biopsy for definitive confirmation.
In summary, fibroadenosis refers to non-cancerous changes in breast tissue that can lead to lumpy or nodular breasts. At the same time, this is a specific type of benign tumor that forms in the breast tissue.
Phyllodes Tumor Vs. Fibroadenoma
Phyllodes tumors and fibroadenomas are both types of breast tumors, but they have distinct characteristics and behaviors. Here’s a brief comparison between Phyllodes tumors and fibroadenomas:
1. Origin and Composition:
– Fibroadenoma: These diseases are benign tumors originating from the breast’s epithelial and stromal tissues. They are composed of both glandular and connective tissues.
– Phyllodes Tumor: These rare tumors also arise from the stromal tissue of the breast. A leaf-like or phyllodes pattern under the microscope characterizes them.
2. Size and Growth:
– Fibroadenoma: This is usually a small, firm, and easily movable. They may remain stable in size, grow slowly, or even regress over time.
– Phyllodes Tumor: Phyllodes tumors can vary in size, and some may multiply. They are often larger than this and may be associated with a faster growth rate.
3. Histological Features:
– Fibroadenoma: Microscopically, this has a well-defined capsule and consists of both glandular and stromal components. They are usually not associated with significant cellular atypia.
– Phyllodes Tumor: Phyllodes tumors have a characteristic leaf-like or staghorn-like pattern under the microscope. They can be classified as benign, borderline, or malignant based on their cellular characteristics and stromal overgrowth.
4. Behavior and Risk of Malignancy:
– Fibroadenoma: These are typically benign and have a shallow risk of transforming into cancer (malignancy).
– Phyllodes Tumor: Phyllodes tumors have a higher potential for malignancy, especially the malignant variants. However, the majority of phyllodes tumors are benign.
5. Treatment:
– Fibroadenoma: The treatment for this disease may include observation, biopsy, or surgical removal if the tumor causes symptoms or raises concerns.
– Phyllodes Tumor: Treatment for phyllodes tumors often involves surgical removal with clear margins. In some cases of malignant phyllodes tumors, additional treatments like radiation therapy may be recommended.
Exploring Health Information and Outreach Through Digital Platforms
In today’s interconnected world, platforms like MedicalNewsToday.com, GetMeGiddy.com, and Explained. Today plays a pivotal role in delivering accessible and accurate health information. These websites provide insights into a range of medical topics, from breast cancer care (as supported by breastcancercare.org.uk) to reproductive and sexual health education, empowering users to make informed decisions about their well-being. Similarly, platforms like iliveok.com and kfd.me provide simplified medical explanations and wellness tips, creating a user-friendly space for everyday health concerns.
On the outreach front, sites like OutreachDashboard.wmflabs.org, cornerstone-house.org.uk, and dayofdifference.org.au focus on community engagement and healthcare outreach, particularly in underserved populations. Tools like Zproxy.org and Glarity.app enhance online access and content clarity, supporting digital inclusion. Meanwhile, platforms such as pkwomensclinic.com.sg and issalute.it offer region-specific healthcare services, reinforcing the value of localized medical support. Together, these digital spaces form a powerful ecosystem of information, care, and community support, making health knowledge more transparent, inclusive, and widely available.
Types Of Fibroadenoma
There are several types of fibroadenomas based on their characteristics, and they are classified primarily by their histological features. Here are some common types:
1. Simple Fibroadenoma:
– This is the most common type of disease.
– It is well-defined and has a uniform appearance under the microscope.
2. Complex Fibroadenoma:
– This type has additional features that make it more complex when examined histologically.
– Features may include cysts, sclerosing adenosis, or epithelial calcifications.
3. Juvenile Fibroadenoma:
– This type is more common in younger women, typically under 30.
– It may be associated with pregnancy or lactation.
4. Giant Fibroadenoma:
– This is a larger variant of the disease, typically greater than 5 cm in size.
– Although benign, its size can cause concern and may warrant removal.
5. Phyllodes Tumor:
– Phyllodes tumors are rare fibroepithelial tumors that can be benign, borderline, or malignant.
– They have a leaf-like or “phyllodes” appearance under the microscope.
– Unlike typical fibroadenomas, phyllodes tumors have a higher potential for recurrence and may require surgical removal.
It’s important to note that while these are generally non-cancerous, any new lump or change in breast tissue should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
How To Diagnose Fibroadenoma?
If you notice a lump in your breast, you should always consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis. Various tests can detect this, such as:
– Breast ultrasound:
This is a painless procedure that utilizes sound waves to develop images of the breast tissue. It can show the size and shape of the lump and distinguish it from a fluid-filled cyst.
– Mammography:
This is an X-ray exam of the breast that can reveal the borders of the lump and its relation to other tissues. However, it may not be very effective for young women who have dense breast tissue, which makes it harder to see the details. Also, mammography involves radiation exposure, so it is not recommended for women under 30 unless there is a strong suspicion of cancer.
– Core needle biopsy:
This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a hollow needle into the lump and taking a small tissue sample for analysis. A doctor can use ultrasound or mammography to guide the needle to the right spot. The tissue sample can confirm if the lump is a fibroadenoma or another type of tumor, such as a phyllodes tumor, which is rare but can be malignant (cancerous).
Based on the outcome of diagnostic tests, your physician may suggest different options for managing your fibroadenoma.
Risk Factors For Fibroadenomas
Some factors that may increase the likelihood of developing fibroadenomas are:
– Young age (<35 years)
– Prior history of benign breast disease
– Obesity
– Family history of multiple diseases.
– Consumption of oral contraceptives before 20
Conclusion
In conclusion, fibroadenomas are common benign breast lumps that primarily affect women of childbearing age. While they are generally non-cancerous, seeking medical attention for proper diagnosis is crucial.
Understanding the symptoms, such as a painless lump, and potential causes, including hormonal changes, can aid in early detection.
Treatment options vary, with some cases requiring no intervention, while others may benefit from surgical removal or monitoring. Regular breast self-exams and routine screenings play a vital role in maintaining breast health, allowing for timely detection and appropriate management of this disease.
Consulting with a medical professional is necessary for personalized guidance and care addressing this and ensuring overall breast well-being.
Fibroadenoma treatment can be expensive, encompassing diagnostic tests, consultations, surgery, or other medical interventions. Crowdfunding allows individuals to reach out to a large number of people, each contributing a small amount, thereby collectively covering the substantial treatment costs.












