Picture this: a loved one is fighting for their life, and the doctor recommends ECMO treatment, stating its potential to turn the tide in their favor. Naturally, the first question that pops into your mind is, “What will it cost?” This blog is here to provide you with a unique and simplified insight into the ECMO treatment cost in India per day. We aim to equip you with the necessary information to make informed decisions while navigating an emotionally and financially challenging time.
In recent years, India has witnessed an exponential rise in the incidence of severe respiratory illnesses and heart-related ailments. Factors like pollution, lifestyle changes, and the pandemic have played pivotal roles in exacerbating these health issues. As a result, the demand for advanced life-saving treatments like ECMO has surged. However, despite the growing demand and undeniable efficacy of ECMO, the cost of the treatment has raised concerns among families and patients. Understanding the expenses associated with ECMO is vital to ensure timely access to this life-saving technology without facing undue financial burden.
In the vast landscape of medical advancements, ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) stands as a shining beacon of hope for patients battling life-threatening respiratory or cardiac conditions. This remarkable technology offers a second chance at life to those facing the most critical situations. However, as miraculous as ECMO treatment may be, it’s crucial to understand its financial implications, especially in a country like India, where healthcare affordability remains a pressing concern.
To provide a clearer picture, we will explore some indicative figures related to ECMO treatment costs in India. It’s important to note that the actual expenses may vary based on several factors, such as the hospital, location, duration of treatment, and the patient’s medical condition.
Knowledge is power, and it becomes invaluable in healthcare decisions. This blog endeavors to bridge the information gap surrounding ECMO treatment costs in India, empowering you to make well-informed choices for your loved ones during critical moments. Our mission is to ensure that financial constraints do not hinder your access to advanced medical care when it matters the most.
EMCO treatment cost in India per day can seem intimidating, but with the correct information, you can face it head-on, prepared and empowered. Our blog seeks to provide a comprehensive and easy-to-understand overview of the expenses involved and valuable insights into funding options that can make this life-saving treatment a reality for those who need it the most.
Remember, life is priceless, and with the proper knowledge, you can embrace hope and navigate the challenging waters of critical healthcare decisions with confidence. Stay informed, stay strong, and let’s stand together in the pursuit of life and well-being.
Also Read: Hemodynamic Monitoring
Table of Contents
ECMO Treatment Cost In India Per Day
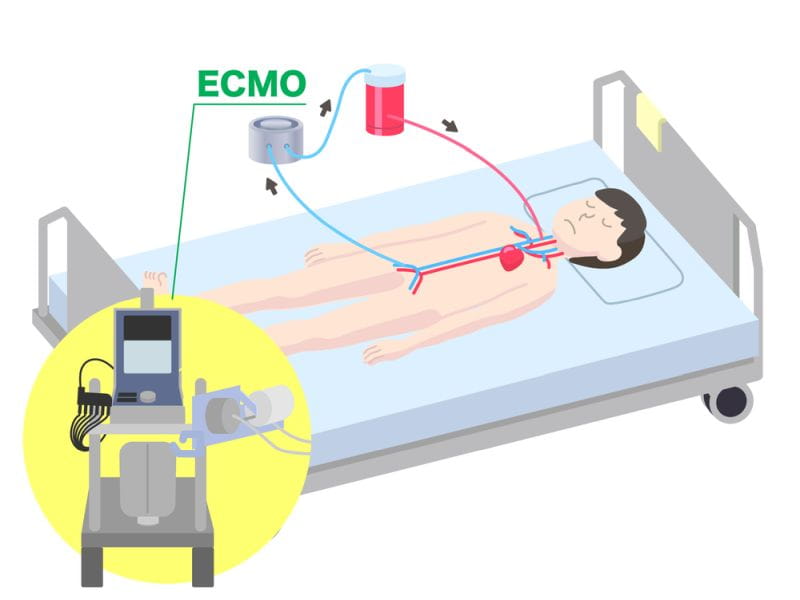
The cost of ECMO treatment in India depends on several factors, such as:
– The type of ECMO treatment (VV or VA)
– The duration of ECMO treatment
– The hospital and its facilities
– The availability of ECMO machines and specialists
– The complexity of the patient’s condition
– The need for additional procedures or medications
On average, the ECMO machine itself costs over 35 lakhs INR, and the ECMO Treatment costs between 80,000–5,00,000 INR per day. However, these costs may vary widely depending on the factors mentioned above. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with your doctor and the hospital staff to get an accurate estimate of the ECMO treatment cost in India per day.
Read More: Impactguru hospital finder tool India
What Is ECMO Treatment?

ECMO, also called Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, is a life-saving medical treatment for patients with severe respiratory or cardiac failure. It is a form of life support that provides temporary oxygenation and circulation support outside the body when the heart and lungs cannot function adequately.
The primary goal of ECMO treatment is to oxygenate the blood & remove carbon dioxide from the body when the patient’s lungs and heart are unable to do so effectively. This can occur for various reasons, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), severe pneumonia, heart failure, congenital heart defects, or complications following significant surgeries.
The ECMO system consists of several essential components:
1. Circuit: The ECMO circuit is the central component that allows blood to flow outside the body through an artificial membrane that performs gas exchange. It consists of two primary tubes – the venous cannula and the arterial cannula.
– Venous cannula: This tube is inserted into a large vein (often the vena cava) and carries deoxygenated blood from the patient’s body to the ECMO machine.
– Arterial cannula: This tube is inserted into a large artery (commonly the aorta or one of its branches) and returns oxygenated blood to the patient’s body.
2. Pump: The ECMO machine has a pump that continuously moves blood through the circuit. The pump helps maintain proper blood flow and ensures adequate oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal.
3. Oxygenator: The oxygenator is a specialized membrane within the ECMO machine that allows for gas exchange. It adds oxygen to the blood & removes carbon dioxide, performing the function of the lungs.
4. Heat Exchanger: The ECMO machine includes a heat exchanger to regulate the blood temperature before it is returned to the patient. This ensures the blood is at the appropriate temperature when it re-enters the body.
ECMO treatment is an invasive procedure requiring highly specialized equipment, expertise, and a team of skilled healthcare professionals. The procedure is typically performed in an intensive care unit (ICU) or a specialized ECMO center. During the treatment, the patient is often sedated and connected to the ECMO machine via the cannulas. Blood is taken from the patient, passed through the oxygenator for gas exchange, and then returned to the patient’s body. This continuous process helps support the heart and lungs, allowing them time to recover and heal.
ECMO treatment is not without risks and complications. Potential complications may include bleeding, infection, clotting issues, and damage to blood cells. Additionally, ECMO requires close monitoring and adjustments to ensure the patient’s condition is improving. ECMO is typically considered a last-resort option when other forms of conventional life support have failed and the patient’s condition is critical. It is a temporary measure and is generally used for a few days to weeks until the underlying condition improves or until other treatment options, such as organ transplantation, become available.
It’s essential to note that ECMO is a complex and resource-intensive treatment, and not all medical facilities can provide it. The decision to initiate ECMO treatment is made on a case-by-case basis by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, considering the patient’s condition and overall prognosis.
Types Of ECMO Treatment
ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) is a life-saving medical treatment that provides temporary support for patients with severe respiratory or cardiac failure. It involves using a machine to oxygenate the blood and eliminate carbon dioxide outside the body, allowing the heart & lungs to rest & heal. There are two main types of ECMO treatment: Venoarterial (VA) ECMO and Venovenous (VV) ECMO. Let’s dive into the details of each:
1. Venoarterial (VA) ECMO:
Venoarterial ECMO is used for patients with both respiratory and cardiac failure. In this method, blood is withdrawn from a large vein (usually the superior or inferior vena cava) and returned to the body through a major artery (usually the aorta or common carotid artery). VA ECMO provides both respiratory and circulatory support, and it is typically used for patients with severe heart failure, cardiogenic shock, or those who need support for both heart and lung function.
VA ECMO can be further categorized into two subtypes based on the cannulation sites:
a. Peripheral VA ECMO: In this configuration, the cannulas (large tubes) are inserted peripherally, usually in the groin or neck vessels. Peripheral VA ECMO is easier and quicker to set up but may have limited blood flow rates, especially if the patient has poor peripheral circulation.
b. Central VA ECMO: Central VA ECMO involves surgically placing the cannulas directly into the heart or the large vessels near the heart. This allows for higher blood flow rates and is preferred for patients with severe heart and lung dysfunction. However, central VA ECMO is more invasive and requires skilled surgical expertise.
2. Venovenous (VV) ECMO:
Venovenous ECMO is used when the patient’s heart is still functioning adequately, but the lungs are severely compromised. Blood is withdrawn from a large vein (usually the inferior vena cava) and returned to another large vein (usually the right atrium). VV ECMO provides only respiratory support, allowing the heart to continue pumping blood through the body.
Like VA ECMO, VV ECMO can also be classified into peripheral and central configurations:
a. Peripheral VV ECMO: In this setup, the cannulas are placed peripherally, often in the groin area or the neck vessels. Peripheral VV ECMO is less invasive and more straightforward to implement but may have limitations in blood flow rates.
b. Central VV ECMO: In central VV ECMO, the cannulas are surgically inserted into large central veins near the heart, like the superior vena cava or right atrium. This configuration allows for higher blood flow rates and is used in patients with more severe lung dysfunction. However, it requires skilled surgical expertise.
ECMO treatment requires a highly specialized team of healthcare professionals, including ECMO specialists, intensivists, nurses, and perfusionists, to manage and monitor the patient throughout the therapy. The decision to use VA or VV ECMO depends on the patient’s specific condition and the judgment of the medical team. ECMO is a complex and resource-intensive therapy, but it has proven to be life-saving for patients facing severe cardiopulmonary failure.
What Is ECMO Treatment Used For?

ECMO is a kind of life support that temporarily takes over the function of the heart & lungs to provide oxygen to the blood and eliminate carbon dioxide when the body’s organs cannot do so adequately. ECMO treatment is typically considered for patients who have failed conventional medical therapies and mechanical ventilation or when those options are not sufficient to support the patient’s failing heart or lungs. It is commonly used in the following situations:
1. Respiratory Failure: ECMO is employed when a patient’s lungs cannot provide adequate oxygenation and ventilation to sustain life, such as in cases of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or serious pneumonia.
2. Cardiac Failure: In severe heart failure or cardiogenic shock, where the heart cannot pump blood effectively to meet the body’s demands, ECMO can temporarily support the heart’s function.
3. Congenital Heart Defects: ECMO can be used in infants born with severe heart defects, providing support until corrective surgery can be performed.
4. Post-Cardiac Surgery: Sometimes, patients may experience severe cardiac dysfunction after heart surgery, and ECMO can support the heart during recovery.
ECMO involves diverting a patient’s blood through an artificial membrane oxygenator, which infuses oxygen into the blood & takes out carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood is restored to the patient’s body, bypassing the failing heart or lungs. ECMO is a complex and resource-intensive treatment typically used as a last resort when other medical interventions have failed. It requires specialized medical personnel and equipment, and its use is carefully considered on a case-by-case basis.
How Does ECMO Work?
Here’s how ECMO works:
1. Cannulation: The first step is to insert catheters, called cannulas, into the patient’s blood vessels. One cannula is kept in a large vein, typically the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava, to withdraw blood from the body. The other cannula is placed in an artery, such as the aorta or femoral artery, to return the oxygenated blood to the body.
2. Pump and Oxygenator: The cannulas are connected to an ECMO machine consisting of a pump and an oxygenator. The pump draws blood from the patient’s body through the venous cannula and pushes it through the oxygenator.
3. Oxygenation: The oxygenator is a critical component that acts as an artificial lung. It takes the blood from the patient and exposes it to a mixture of oxygen, removing carbon dioxide (CO2) and adding oxygen to the blood. This process mimics the function of the lungs, allowing the blood to be adequately oxygenated.
4. Return of Oxygenated Blood: Once the blood is oxygenated, it is returned to the patient’s body through the arterial cannula, providing the necessary oxygen to the organs and tissues.
5. Continuous Monitoring: Throughout the ECMO treatment, the patient’s blood pressure, oxygen levels, and other vital signs are closely monitored to ensure the ECMO machine is working correctly and that the patient’s condition is stable.
ECMO is typically used for short-term support, often for a few days to weeks, while the underlying condition causing the heart or lung failure is treated and resolved. A team makes the decision to initiate ECMO of specialized healthcare professionals and is usually considered when all other treatments have failed to provide adequate support.
It’s essential to note that ECMO is a complex, high-risk procedure generally reserved for critically ill patients. The management of ECMO requires specialized training and expertise, and the outcomes can vary depending on the underlying condition and the patient’s overall health.
What Are The Symptoms In Patients Who Need ECMO?
The specific symptoms and conditions that may indicate the need for ECMO can vary, but generally, patients who require ECMO may exhibit some or all of the following symptoms:
1. Severe Respiratory Distress: Patients may have extreme difficulty breathing, rapid or difficult breathing, and may require insufficient mechanical ventilation to maintain adequate oxygen levels.
2. Acute Respiratory Failure: ECMO may be considered when a patient’s lungs fail to oxygenate the blood properly, leading to dangerously low oxygen levels in the body.
3. Severe Cardiac Failure: In some cases, ECMO may be utilized for patients with severe heart failure that is unresponsive to other treatments.
4. Refractory Hypoxemia: Patients with low oxygen levels in the blood (hypoxemia) that does not improve despite maximum conventional respiratory support may require ECMO.
5. ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome): ECMO is often considered for patients with severe ARDS, a life-threatening lung condition that can occur due to various causes, including pneumonia, sepsis, trauma, or other critical illnesses.
6. Cardiogenic Shock: This condition occurs when the heart cannot drive enough blood to meet the body’s needs, leading to organ failure. ECMO may be used temporarily while the underlying cause is treated.
7. Post-Cardiac Arrest: After a cardiac arrest, ECMO can sometimes be employed to support the heart and lungs during recovery.
8. Bridge to Transplant: ECMO may be used as a bridge to keep a patient stable while awaiting a heart or lung transplant.
Diagnostic Tests Performed Before ECMO

Before initiating Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO), several tests and assessments are typically performed to ensure that the patient is a suitable candidate for the medical procedure & to optimize the chances of a successful outcome. These pre-ECMO tests may vary depending on the patient’s condition & the clinical judgment of the healthcare team. Here are some common tests and assessments that are often conducted before ECMO initiation:
1. Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) analysis: ABG tests provide critical information about the patient’s acid-base balance, oxygenation, and ventilation status.
2. Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures the levels of various blood cells and can help identify potential causes of the patient’s condition, such as infection or anemia.
3. Coagulation profile: This test assesses the blood’s ability to clot and helps determine the risk of bleeding or clotting complications during ECMO support.
4. Blood chemistry panel: A comprehensive panel of blood tests that assesses the patient’s electrolyte balance, liver function, kidney function, and overall metabolic status.
5. Chest X-ray or CT scan: These imaging studies help assess the condition of the lungs and chest cavity and can provide valuable information about the underlying lung disease.
6. Echocardiography: This ultrasound-based test allows visualization of the heart’s structure and function, helping identify cardiac issues that may impact the ECMO candidacy or management.
7. Hemodynamic monitoring: Continuous monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs to assess the patient’s hemodynamic stability.
8. Pulmonary function tests: These tests measure lung capacity and function, which helps evaluate the severity of respiratory failure and the potential for lung recovery.
9. ECG (Electrocardiogram): This test records the heart’s electrical activity and can identify arrhythmias or other cardiac issues.
10. Infectious disease screening: To check for infections that may affect ECMO candidacy or require specific treatment.
11. Cross-matching blood for potential transfusions: To ensure compatible blood products are available during ECMO support.
12. Psychosocial assessment: An evaluation of the patient’s mental health and social support system to gauge their ability to cope with the ECMO procedure and recovery.
These tests help the medical team assess the patient’s overall health status, identify potential contraindications or risks, and tailor the ECMO support to the patient’s specific needs. ECMO is a complex and invasive procedure, so a comprehensive evaluation is essential to make well-informed decisions about its initiation and management.
Benefits Of ECMO Treatment
ECMO is typically used in critical situations when other treatment options have failed. Some of the benefits of ECMO treatment include:
1. Oxygenation and Carbon Dioxide Removal: ECMO provides a reliable means of oxygenating the blood and removing excess carbon dioxide. It can effectively support patients whose lungs are severely damaged, allowing their bodies to receive oxygen.
2. Support During Recovery: ECMO can provide vital support while a patient’s heart or lungs heal from injury or illness. By temporarily taking over the organ’s function, it reduces the workload on these organs and gives them time to recover.
3. Bridge to Transplant: For patients awaiting a heart or lung transplant, ECMO can serve as a “bridge” to keep them stable and alive until a suitable donor becomes available.
4. Time for Other Treatments: ECMO can provide time for other medical interventions, such as antibiotics or surgeries, to take effect. It helps stabilize the patient’s condition during these critical periods.
5. Improved Survival Rates: In certain situations, ECMO can vastly improve the chances of survival for patients with serious cardiac or respiratory failure who would otherwise have a very low chance of making it through without this intervention.
6. Support for Special Populations: ECMO can be used in neonates and pediatric patients with life-threatening conditions, providing essential support for their underdeveloped organs until they mature or receive necessary treatments.
Are There Any Risks With ECMO Treatment?

Yes, ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) is a life-saving medical treatment used in critical situations but without risks. ECMO is typically used for patients with severe respiratory or cardiac failure when conventional therapies are not sufficient. Some of the potential risks & complications associated with ECMO treatment include:
1. Bleeding: Anticoagulants are used during ECMO to prevent clotting in the circuit, but this can increase the risk of bleeding in the patient. Bleeding complications can be severe and may require blood transfusions or surgical interventions.
2. Infection: The ECMO circuit creates an artificial connection to the patient’s bloodstream, increasing the risk of infection. Infections can range from localized infections at the cannulation site to systemic conditions like sepsis.
3. Blood clots: Despite anticoagulation, there is a risk of blood clots forming within the ECMO circuit, leading to complications like circuit malfunction or embolism.
4. Organ damage: Prolonged ECMO support may cause organ damage due to decreased blood flow or oxygenation during the treatment.
5. Hemolysis: The mechanical forces within the ECMO circuit can cause the breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis), leading to anemia and potential kidney problems.
6. Hemodynamic instability: Changes in blood pressure and circulation during the initiation or weaning off of ECMO can lead to hemodynamic instability.
7. Air embolism: Air can inadvertently enter the ECMO circuit, potentially causing air embolism, a condition in which air bubbles obstruct blood flow.
8. Circuit-related complications: Malfunctions in the ECMO circuit or equipment can occur, leading to the need for circuit changes or replacements.
9. Neurological complications: There is a risk of neurological problems associated with ECMO treatment, such as stroke or cognitive impairment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) treatment is an advanced life-saving procedure used to support patients with severe heart or lung problems. The availability of ECMO in India has expanded significantly in recent years, making it more accessible to those in need. While the cost of ECMO treatment in India can be relatively high, it is still more affordable than in many other countries.
Patients and their families can consider various options to manage the ECMO treatment cost-effectively. First, they can explore government or private healthcare schemes that offer financial assistance for critical treatments like ECMO. Second, many hospitals offer payment plans or installment options, making it more manageable for families to bear the financial burden. Lastly, seeking support from charitable organizations or crowdfunding platforms can be a viable option to raise funds for ECMO treatment.
It is also worth mentioning that the cost of ECMO treatment should not be the sole factor guiding the decision-making process. The medical team’s expertise, the quality of care provided, and the hospital’s success rate in handling ECMO cases are equally important considerations. In summary, while ECMO treatment in India may be costly, it provides a lifeline to patients facing life-threatening heart or lung conditions.
When facing life-threatening situations like ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) treatment, finances should not stand in the way of hope and healing. The crowdfunding platform provides a powerful solution to this dilemma, enabling anyone in need to access high-cost ECMO treatment in India.












