Cancer, a formidable adversary affecting millions worldwide, continues to be a prevalent concern in the realm of healthcare. With its devastating impact on individuals and communities, understanding this multifaceted disease becomes crucial. This comprehensive blog post delves into the intricate world of cancer, exploring its diverse dimensions, including cancer symptoms, causes, stages, prevention, and diagnosis. Whether you seek information to protect yourself and your loved ones or simply desire a deeper understanding of this pervasive condition, this article aims to provide you with valuable insights. Brace yourself for an enlightening journey through the intricacies of cancer, empowering you with the knowledge to confront this formidable foe head-on.
Table of Contents
Symptoms Of Cancer

Recognizing the symptoms associated with cancer is essential for early detection and prompt medical intervention. It’s important to note that the specific signs and symptoms can differ depending on the kind and stage of cancer and individual factors. However, there are common signs & symptoms that may indicate the presence of cancer. Let’s explore them in detail:
1. Sudden Weight Loss: Sudden and unexplained weight loss, primarily if it occurs without diet or physical activity changes, can be a potential sign of cancer. Significant weight loss, typically defined as losing 10 pounds or more without intending to, may be associated with several kinds of cancer, such as pancreatic, stomach, lung, or ovarian cancer.
2. Fatigue: Persistent fatigue, feeling tired or weak even after getting enough rest, can be a cancer symptom. Cancer-related fatigue is different from normal tiredness and can be severe and debilitating. It may be caused by cancer treatments like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other factors associated with the disease.
3. Pain: Chronic or persistent pain is a common cancer symptom. The pain may originate from the tumor pressing against nerves, bones, or organs. It can change in intensity and location depending on the type and stage of cancer. For example, bone cancer may cause deep, aching pain, while headaches can be a symptom of brain tumors.
Read More – A Closer Look at Invasive Cancer: Information & Insights
4. Changes in the Skin: Skin changes can be indicative of certain types of cancer. These changes may include darkening or yellowing of the skin (jaundice), excessive hair growth, changes in the appearance of moles or skin lesions, or the development of new skin abnormalities. Skin cancer, such as melanoma, often presents as changes in the color, size, or shape of existing moles or the appearance of new growths.
5. Unusual Bleeding: Unexplained bleeding or unusual discharge can be warning signs of cancer. For example, blood in the stool or urine may indicate colorectal or bladder cancer, while abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge can be associated with gynecological cancers. Coughing up blood may be a sign and symptom of lung cancer.
6. Persistent Cough or Hoarseness: A persistent cough that lingers for several weeks or a hoarse voice that doesn’t improve can be a sign of lung, throat, or laryngeal cancer. While coughs and hoarseness can also result from other non-cancerous conditions, it is essential to contact a medical professional for proper evaluation and detection.
7. Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Unexplained changes in bowel or bladder habits should not be ignored. This can include persistent diarrhea or constipation, changes in stool consistency or color, blood in the stool, or urinary symptoms like frequent urination, urgency, or blood in the urine. These symptoms can be associated with colorectal, bladder, or prostate cancer.
8. Difficulty Swallowing or Indigestion: Persistent difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia or chronic indigestion, can be a symptom of esophageal, stomach, or throat cancer. These symptoms may be accompanied by pain or a feeling of discomfort in the chest or abdomen.
9. Persistent Infections or Fevers: Frequent infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, can sometimes be a sign of underlying cancer, particularly in individuals with a weakened immune system. Additionally, certain types of cancer can cause recurring fevers, especially in the absence of other explanations.
10. Other General Symptoms: Cancer can also present with general symptoms such as unexplained nausea or vomiting, unexplained changes in appetite, unexplained swelling or lumps, persistent headaches, or unexplained neurological symptoms like dizziness or seizures. While these symptoms can be associated with various conditions, they should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
It’s important to remember that experiencing one or more of these symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean you have cancer. Many of these cancer symptoms can also be caused by non-cancerous conditions. However, if you notice any persistent or concerning symptoms, it is always good to contact a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Early detection of cancer plays a crucial role in successful treatment outcomes. Regular screenings and check-ups are vital, especially if any of your family had cancer or other risk factors.
Causes Of Cancer
Cancer is a deadly disease with multiple factors contributing to its development. While the exact causes of cancer can vary from individual to individual, several common factors have been identified as potential contributors. It’s important to note that cancer is often caused by a combination of multiple factors rather than a single cause. Let’s explore the various causes of cancer in detail:
1. Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic mutations inherited from parents can increase the risk of developing cancer. These mutations can be passed down from descendent and make individuals more susceptible to certain types of cancer. However, it’s crucial to remember that having a genetic predisposition does not guarantee the development of cancer, as other factors also play a role.
2. Exposure to Carcinogens: Carcinogens are substances or agents that can potentially cause cancer. Exposure to carcinogens can occur through various means, including environmental factors, occupational hazards, lifestyle choices, and medical treatments. Examples of carcinogens include tobacco smoke, asbestos, certain chemicals, ionizing radiation (such as X-rays and UV radiation), and some viruses and bacteria.
3. Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices: Certain lifestyle choices can increase the risk of developing cancer. These include tobacco and alcohol use, poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and excessive exposure to the sun or tanning beds. Tobacco consumption is one of the primary causes of preventable cancer deaths, with smoking linked to various types of cancer, including lung, throat, mouth, bladder, and pancreatic cancer. Additionally, a poor diet lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with excessive consumption of processed and red meats, has been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers.
4. Chronic Inflammation: Long-term inflammation in the body can contribute to the development of cancer. Chronic inflammation can result from various factors, such as untreated infections, certain autoimmune diseases, and conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammation causes changes in the DNA and increases cell turnover, increasing the chances of mutations that can lead to cancerous cell growth.
5. Infections: Some infections have been linked to a high risk of certain types of cancer. Viruses like human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis B and C viruses, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can increase the risk of developing specific cancers. For example, HPV is a known cause of cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancer, while chronic hepatitis B and C infections can lead to liver cancer.
6. Hormonal Factors: Hormonal imbalances or prolonged exposure to certain hormones can contribute to cancer development. For example, long-term use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in postmenopausal women has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. Similarly, women with early menarche (first menstruation) or late menopause have a slightly higher risk of developing breast cancer due to prolonged exposure to estrogen.
7. Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors can increase the risk of cancer. This includes exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and toxins present in the air, water, soil, and workplace. For instance, exposure to asbestos has been linked to lung cancer and mesothelioma, while prolonged exposure to certain chemicals like benzene or formaldehyde can increase the risk of leukemia or other cancers.
8. Age and Family History: Advancing age is a significant risk factor for cancer. As we age, the cumulative effects of various environmental & genetic factors increase the likelihood of developing cancer. Additionally, having a family history of certain types of cancer, especially in first-degree relatives (parents, siblings, children), can increase an individual’s risk of developing the disease.
It’s important to remember that while these factors can contribute to the development of cancer, not everyone exposed to them will develop the disease. The interaction between genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices is complex and unique to each individual. Additionally, some cancer cases may have no identifiable cause, highlighting the need for ongoing research in this field.
Understanding the causes of cancer empowers individuals to make informed choices and adopt preventive measures. Individuals can take proactive measures towards reducing their risk of developing cancer by reducing exposure to carcinogens, adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying vigilant about regular screenings, and seeking prompt medical attention for concerning symptoms.
Stages Of Cancer
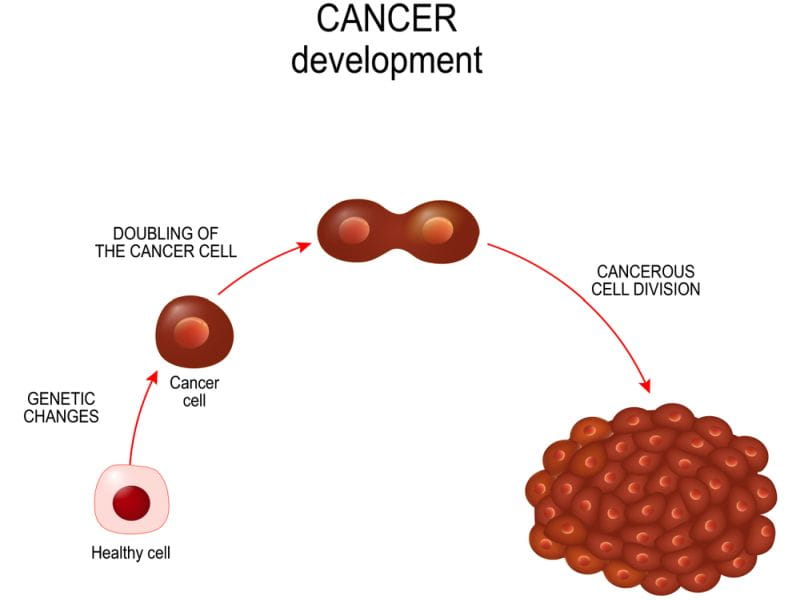
Cancer is typically categorized into different stages to describe how much the disease has progressed. The staging system helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate treatment options and predict the prognosis for individuals with cancer. It’s important to note that the specific stages and treatment approaches can differ depending on the types of cancer. However, we will present a general overview of the stages and common treatment modalities.
Stage 0: Carcinoma in Situ
Stage 0, also called carcinoma in situ, refers to the presence of abnormal cells that have not invaded nearby tissues. In this early stage, cancer cells are confined to the site of origin and have not spread to surrounding areas or distant organs. The primary goal of treatment at this stage is to remove or destroy the abnormal cells to prevent them from progressing into invasive cancer. Common treatment options for stage 0 cancer include:
1. Surgery: Surgical removal of the abnormal cells is often the mainstay of treatment for carcinoma in situ. The goal is to altogether remove the abnormal tissue and achieve negative surgical margins. Based on the kind and tumor location, various surgical techniques may be employed, such as lumpectomy (removal of a localized tumor) or wide local excision.
2. Radiation Therapy: In most instances, radiation therapy may be recommended following surgery to target any remaining abnormal cells or reduce the risk of recurrence. This localized treatment uses high-energy radiation beams to destroy cancer cells.
3. Targeted Therapy: Depending on the specific characteristics of cancer, targeted therapies may be used to inhibit specific molecular targets or pathways involved in cancer development. These therapies interfere with the abnormal signaling mechanisms that promote cell growth and division.
Stage I and Stage II: Localized Cancer
Stage I and II cancers are characterized by the presence of a tumor that is limited to the primary site and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. In these early stages, the tumor is generally smaller in size and has not infiltrated surrounding tissues extensively. The primary treatment modality for localized cancer is often surgery, with the goal of removing the tumor completely. Additional treatments may also be employed based on the characteristics of the cancer. Common treatment options for stage I and II cancer include:
1. Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is typically the initial treatment approach for localized cancer. The kind of surgery will be fixed based on the location & type of the cancer. For example, breast cancer may be treated with a lumpectomy or mastectomy, while prostate cancer may be treated with a prostatectomy.
2. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be prescribed after surgery to kill any remaining cancer tumors in the area or to reduce the risk of local recurrence. It can also be utilized as the standard treatment modality for certain types of cancer unsuitable for surgery.
3. Adjuvant Therapy: Adjuvant therapy refers to additional treatments given after the primary treatment to eliminate any remaining cancer cells or reduce the risk of recurrence. This may include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or hormone therapy, depending on the specific characteristics of the cancer. Adjuvant treatment targets any potential microscopic cancer tumors that may have developed beyond the primary tumor.
Stage III: Regional Spread
Stage III cancer indicates that the tumor has moved to nearby lymph nodes or tissues but has not yet reached distant organs. The extent of lymph node & the size and invasiveness of the tumor can vary within this stage. The treatment approach for stage III cancer typically involves a combination of treatments. Common treatment options for stage III cancer include:
1. Surgery: Surgery may still play a role in stage III cancer, particularly for removing the primary tumor and involved lymph nodes. Surgery may sometimes be performed before or after other treatments, like chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
2. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is often used with surgery or as the primary treatment modality for stage III cancer. It may be employed to target the primary tumor site, involved lymph nodes, and nearby tissues in eliminating any remaining cancer cells.
3. Systemic Therapy: Systemic therapy includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. These treatments are administered through the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body. They are used to target cancer cells that may have spread beyond the primary tumor site. The specific choice of systemic therapy depends on the type of cancer and its molecular characteristics. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill or inhibit the growth of cancer cells, targeted treatment focuses on specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth, and immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
Stage IV: Metastatic Cancer
Stage IV, also known as metastatic or advanced cancer, is characterized by the spread of cancerous cells to distant organs or tissues. In this stage, cancer has the potential to impact different organs and systems in the body. Treatment for metastatic cancer aims to control the disease, alleviate symptoms, and improve the individual’s quality of life. Common treatment options for stage IV cancer include:
1. Systemic Therapy: Systemic therapy remains the primary treatment modality for metastatic cancer. This includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy, based on the type of cancer and its molecular characteristics. The choice of systemic therapy aims to slow cancer progression, manage symptoms, and improve survival rates.
2. Radiation Therapy: It may be used to target specific sites of metastasis to relieve pain, control bleeding, or alleviate other symptoms associated with the spread of cancer. It is often employed in combination with systemic therapy.
3. Surgery: In most cases, surgery may be performed to remove isolated metastases or alleviate symptoms caused by the spread of cancer. This can be particularly helpful when a limited number of metastases are present and can be surgically resected.
4. Palliative Care: Palliative care is crucial in managing symptoms, providing pain relief, and offering emotional and psychological support for individuals with advanced cancer. Palliative care focuses on enriching the quality of life and addressing the disease’s physical, emotional, and social aspects.
It’s important to note that the stage of cancer and the treatment options may be further influenced by individual factors such as overall health, age, and specific characteristics of cancer, including molecular markers and genetic mutations. The treatment plan is typically determined through a multidisciplinary approach involving a team of healthcare professionals specializing in oncology, surgery, radiation therapy, and other relevant disciplines.
Advancements in cancer research and treatment have led to the development of targeted therapies & immunotherapies that can be used in various stages of cancer, including metastatic disease. These treatments offer new possibilities and improved outcomes for cancer patients across different stages of the disease.
In conclusion, the stages of cancer provide crucial details about the extent of the disease and guide treatment decisions. From early stages with localized tumors to advanced stages with metastasis, the treatment approaches evolve to address the specific needs of each stage. Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care are among the commonly used treatment modalities. By tailoring the treatment plan to the stage and characteristics of cancer, healthcare professionals strive to provide the most effective and personalized care for individuals battling this disease.
Ways To Prevent Cancer

Cancer is a genetic disease characterized by the abnormal growth and spread of abnormal cells. While genetics and certain risk factors contribute to its development, adopting a healthy lifestyle and implementing protective measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing various types of cancer. This guide will explore evidence-based strategies and lifestyle choices that can help prevent cancer.
1. Tobacco and Alcohol:
Tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco, is a leading cause of cancer. Quitting smoking & avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce the risk of lung, mouth, throat, and other cancers. Limiting alcohol consumption is also crucial, as excessive drinking is associated with a high risk of several kinds of cancer, including breast, liver, and colorectal cancer.
2. Healthy Diet:
Eating a well-balanced, nutritious diet is paramount in cancer prevention. Incorporate the following guidelines into your diet:
a. Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables, aiming for at least five servings daily. These include essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help protect against cancer.
b. Choose whole grains over refined grains, as they provide more fibre, vitamins, and minerals.
c. Reduce red meat consumption and use lean protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, and lentils.
d. Minimize processed and high-sugar foods, as they are associated with a high risk of certain cancers.
e. Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water each day.
3. Physical Activity:
Regular physical activity plays an important role in cancer prevention. Try to aim for at least 150 minutes of average-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise every week. Engage in activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, or dancing. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, boosts immunity, & reduces the risk of various cancers, including breast, colon, and lung cancer.
4. Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in cancer prevention. Obesity increases the risk of different kinds of cancer, such as breast, colorectal, ovarian, and pancreatic cancer. To achieve and maintain a healthy weight:
a. Follow a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
b. Engage in regular physical activity to burn calories and increase muscle mass.
c. Limit high-calorie, processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive portions.
d. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
5. Sun Protection:
Skin cancer is one of the most evitable types if properly cared for. Protect your skin from harmful Ultraviolet radiation by following these guidelines:
a. Limit sun exposure between 10 am and 4 pm when the sun’s rays are the strongest.
b. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or more to all affected skin areas, even on cloudy days.
c. Wear protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, and sunglasses.
d. Seek shade whenever possible, especially during peak sun hours.
e. Avoid using tanning beds, as they emit harmful UV radiation.
6. Vaccinations:
Certain vaccines can significantly reduce the risk of developing specific types of cancer:
a. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine helps prevent cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers. It is prescribed for both males and females before they become sexually active.
b. Hepatitis B vaccine reduces the risk of liver cancer. It is essential for high-risk individuals, including healthcare workers and those with multiple sexual partners.
c. Consult with your healthcare provider to ensure you are up to date with the prescribed vaccines for your age and circumstances.
7. Regular Screenings:
Screenings aim to detect cancer at an early stage when it is most treatable. Undergo routine screenings for various types of cancer, such as breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancer. Discuss with your medical provider the appropriate screening schedule based on age, gender, and family history.
8. Stress Management And Mental Well-being:
Chronic stress and poor mental health can weaken the immune system and increase cancer risk. Inculcate stress management techniques into your daily routine, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Seek support from loved ones, and consider counseling or therapy if needed.
Preventing cancer requires a proactive approach that involves making healthy lifestyle choices and adopting preventive measures. By avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, keeping a healthy weight, engaging in frequent physical activity, protecting your skin from the sun, receiving appropriate vaccinations, undergoing regular screenings, and managing stress effectively, you can considerably limit your risk of getting cancer.
Empower yourself with knowledge, take charge of your health, and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance. Remember, prevention is critical, and small changes in your daily habits can significantly impact your overall well-being and cancer risk reduction.
Cancer Diagnosis
A cancer diagnosis is a complex and critical step in managing the disease. Timely and accurate diagnosis allows for appropriate treatment planning and better outcomes for patients. Now, we will delve into the various aspects of cancer diagnosis, including the diagnostic process, common techniques and tests used, and the significance of early detection.
1) Diagnostic Process:
The cancer diagnostic process typically involves several steps, including the following:
a. Medical History and Physical Examination:
The initial step involves thoroughly evaluating the patient’s medical history, including family history of cancer, previous medical conditions, and symptoms. A comprehensive physical examination is conducted to assess the presence of any abnormalities or signs indicative of cancer.
b. Diagnostic Tests and Imaging:
Diagnostic tests and imaging techniques visualize and evaluate potential cancerous growths. These may include:
– Blood tests: They can detect certain tumor markers or abnormalities that may suggest the presence of cancer.
– Imaging tests: Techniques such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), & ultrasound can offer detailed images of internal organs and tissues to identify abnormalities.
– Endoscopy: This procedure involves using a flexible tube with a camera to evaluate the inside of organs or body cavities.
– Biopsy: A tissue sample is collected for analysis to decide the presence of cancer cells and their characteristics.
c. Pathology and Laboratory Analysis:
The collected biopsy or tissue samples are sent to a laboratory for pathological analysis. Pathologists examine the samples under a microscope, perform molecular testing, and assess the characteristics of the cells, such as their type, grade, and stage. These findings are crucial in determining the diagnosis and guiding treatment decisions.
d. Cancer Staging:
Cancer staging involves determining the extent and spread of the disease. It helps in planning the most appropriate treatment strategy. Staging is based on various factors, including the tumor’s size and location, lymph node involvement, and the presence of metastasis.
2) Common Diagnostic Techniques and Tests:
Several diagnostic techniques and tests play a vital role in cancer diagnosis. These include:
a. Imaging Techniques:
i. X-rays: This non-invasive technique uses low-dose radiation to create images of bones, tissues, and organs.
ii. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: It provides detailed cross-sectional body images using X-rays and computer processing.
iii. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): It uses a powerful magnetic field and radiowaves to generate detailed images of the body’s structures.
iv. Ultrasound: Sound waves are used to create real-time images of organs and tissues.
b. Biopsy:
i. Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA): A thin needle extracts cells or fluid from a suspicious area for examination.
ii. Core Needle Biopsy: A larger needle extracts a small tissue sample for analysis.
iii. Surgical Biopsy: A surgical procedure removes a larger piece of tissue for examination.
c. Laboratory Tests:
i. Blood Tests: These may include tumor marker tests, complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests, and genetic testing.
ii. Molecular Testing: Techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) analyze genetic and molecular changes in cancer cells.
d. Endoscopy:
i. Upper Endoscopy: It involves using a thin, flexible tube to evaluate the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the small intestine.
ii. Colonoscopy: A long, flexible tube is used to visualize the entire colon and rectum.
iii. Bronchoscopy: It allows examination of the airways and collection of tissue samples for analysis.
3) Significance of Early Detection:
Early diagnosis of cancer is crucial for successful treatment and improved outcomes. Benefits of early diagnosis include:
a. Increased treatment options: Early-stage cancers often have more treatment options available, including less invasive procedures and a higher chance of curative treatment.
b. Better prognosis: Early detection allows for timely intervention, leading to higher survival rates and improved quality of life.
c. Reduced treatment intensity: Detecting cancer at an early stage may minimize the need for aggressive treatments like extensive surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
d. Potential for prevention: Some precancerous conditions can be detected early and treated to prevent cancer development.
4) Advancements in Cancer Diagnosis:
a. Liquid Biopsies: These non-invasive tests detect tumor-derived materials in the blood, such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and cell-free DNA (cfDNA). Liquid biopsies provide valuable information about tumor mutations, treatment response, and the presence of minimal residual disease.
b. Imaging Innovations: Advanced imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), PET-CT, and PET-MRI, offer enhanced sensitivity and specificity for detecting cancer and assessing its spread.
c. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of imaging and molecular data, aiding in the detection and diagnosis of cancer. AI can also assist pathologists in analyzing histopathology samples, potentially reducing diagnostic errors.
A cancer diagnosis is a multi-step process involving medical history evaluation, physical examination, diagnostic tests, imaging techniques, pathology analysis, and cancer staging. Understanding the significance of early detection and the various diagnostic methods available is essential. Prompt diagnosis allows for timely and appropriate treatment planning, leading to better outcomes for patients. If you suspect any signs or symptoms of cancer, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional promptly. Remember, early detection can save lives and increase the chances of successful treatment.
Conclusion

Cancer is a fatal and multifaceted disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This article has offered a broad overview of cancer, covering its symptoms, causes, stages, prevention strategies, and diagnostic process. Individuals can take proactive measures to protect their health by understanding these crucial aspects, while healthcare professionals can improve early detection and provide targeted treatments.
Cancer symptoms can differ depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common signs include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, persistent pain, changes in the skin, abnormal bleeding, and the presence of lumps or tumors. Individuals must be aware of these symptoms and seek medical attention if they persist, as early diagnosis greatly increases the chances of successful treatment.
The causes of cancer are multifactorial, with a blend of genetic and environmental factors leading to its development. Understanding the stages of cancer is crucial for determining appropriate treatment plans and predicting outcomes. Staging involves assessing the size of the tumor, its spread to nearby lymph nodes, and the presence of metastasis in distant organs.
Prevention is an essential component in the fight against cancer. Individuals can limit their risk of developing the disease by implementing preventive measures. Regular screenings and check-ups allow for early detection of precancerous or cancerous conditions, enabling timely intervention.
The cancer diagnosis involves a comprehensive process aimed at confirming the disease’s presence, type, location, and stage. Screening tests are employed to identify cancer in its early stages, while further diagnostic methods, such as imaging techniques, laboratory tests, and molecular testing, provide more detailed information. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing appropriate treatment plans and predicting patient outcomes.
Advancements in cancer diagnosis continue to revolutionize the field. Liquid biopsies, which detect tumor-derived materials in the blood, offer a non-invasive method for monitoring treatment response and detecting minimal residual disease. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms assist in analyzing vast amounts of data, aiding in detecting, diagnosing, and interpreting cancer-related information.
Finally, a comprehensive understanding of cancer—from its symptoms and causes to the different stages, preventive measures, and diagnostic procedures—is essential for individuals and healthcare professionals. By recognizing the early signs, adopting a healthy lifestyle, undergoing regular screenings, and staying informed about the new advancements in diagnosis and treatment, we can collectively strive to reduce the burden of cancer and improve patient outcomes. Together, we can put efforts towards a future where cancer disease is preventable, curable, or effectively managed, offering hope and better quality of life for those affected by this challenging disease.
Are you or someone you know who is struggling to cover the high cost of cancer treatment in India? Crowdfunding offers a powerful solution to alleviate the financial burden and ensure access to essential medical care. Crowdfunding platform like ImpactGuru can help individuals cover the high cost of cancer treatment in India by providing a trusted medium to raise funds from a vast network of people. By leveraging the power of community, social media, and transparent fundraising platforms, individuals can raise the necessary funds, receive emotional support, and navigate the challenging journey with hope and financial relief.












